
views
Beijing: Nearly 40 geologists from China and Pakistan have teamed up to survey the Makran Trench in Balochistan following Beijing's concerns over the possibility of a massive earthquake affecting the strategic Gwadar port in the volatile province, a media report said on Saturday.
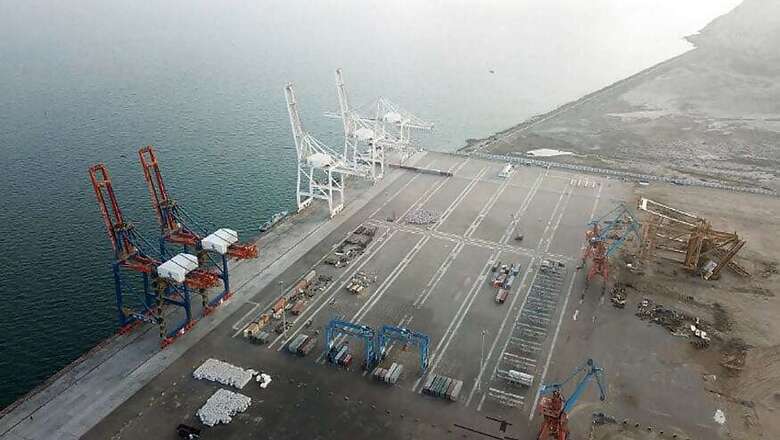
The trench is the meeting point for two tectonic plates and is close to the Pakistani deep-sea port of Gwadar which China has acquired on a 40-year lease.
Gwadar forms part of the important link for the over USD 50 billion China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) connecting to China's Xinjiang province through the Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK).
"It has been more than 70 years since the last big earthquake shook the Makran Trench off the south coast of Pakistan but if and when the next catastrophic one happens, it could disturb more than the landscape," the Hong-Kong based South China Morning Post reported.
Any potential disaster in the area could undermine Beijing's ambitions to revive trade from China through Asia to Africa and Europe through Gwadar port, the report said. That is why scientists from China and Pakistan have teamed up to survey the trench and assess the dangers lurkingin the deep, it said.
The trench is a seismically active zone in the Arabian Sea where one plate is inching beneath the other in a "subduction zone".
The last major earthquake was of 8.1 magnitude in 1945, which triggered a tsunami that battered Iran, Pakistan, Oman and India and killed around 4,000 people.
Last year, a 6.3-magnitude quake hit the area. Despite the damage, not much is known about the zone. Seismologist Yang Hongfeng from Chinese University of Hong Kong said scientific expeditions in this part of the ocean were quite rare.
"A lot of important scientific questions remain unanswered," Yang said.
"The results will definitely advance our understanding [while] providing critical data to reduce the risk in the region," he was quoted as saying in the report. The quest is to get a better understanding of the subduction zone, which scientists say is unusual in part because it has a deposit of soft sediment several kilometres thick, Yang said.
To find answers, roughly 40 researchers from the two countries boarded the Experimental 3-vessel for the trench last month, lowering instruments into the waters to do a "CT scan" of the Earth's structure.
The expedition was a joint effort by the South China Sea Institute of Oceanology in Guangzhou and the National Institute of Oceanography (NIO)in Pakistan. It was funded largely by the Chinese government-funded Chinese Academy of Sciences, said Asif Inam, NIO director general.
"The information and data being collected during the expedition would make a significant contribution to coastal developers and planners," Inam told South China Morning Post. The threat of an earthquake near the port is a big concern for both countries.
"There's a whole lot at stake. The port, if fully developed and operationalised, can be a critical asset for Pakistan, and there's no nation that Pakistan would be more comfortable entrusting it to than its close friend China," Michael Kugelman, said a senior associate for South Asia at the US-based think tank Wilson Centre.
Kugelman said the destructive impact that an earthquake or tsunami could have on the operations of the port should not be overstated, given that actual operations were still limited.
"Still, given issues of proximity and general vulnerability Pakistan doesn't cope or respond well to natural disasters, given a lack of resources and incapacity there's certainly reason to believe that intense earthquake activity would pose a clear and present danger to Gwadar," he was quoted as saying in the report.


















Comments
0 comment