views
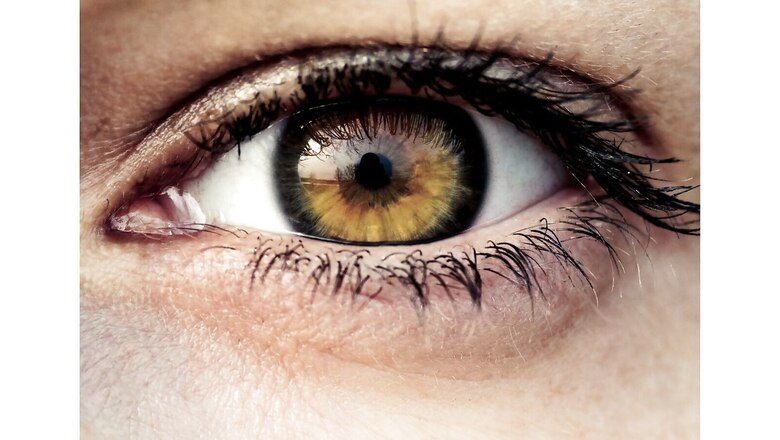
A research published in the journal Eye shows how artificial intelligence (AI) machine learning can detect diabetic retinopathy in its early stages, which is a primary cause of avoidable blindness, especially in asymptomatic individuals.
Recently, a team of researchers from the Medical University of Vienna’s Department of Ophthalmology and Optometry undertook a study to evaluate autonomous AI-based screening against human-graded ultra-widefield colour fundus pictures for premature diabetic retinopathy staging in asymptomatic individuals. The study was led by Aleksandra Sedova of the Medical University of Vienna.
The study comprised 54 people with asymptomatic diabetes mellitus who had never been diagnosed with DR. The patients ranged in age from 18 to 80. There were 32 patients with type 2 diabetes (11 women) and 20 individuals with type 1 diabetes (8 women). For two individuals, the type of diabetes was uncertain. These patients’ ultra-widefield (UWF) colour fundus pictures were included in the prospective observational pilot trial.
A server-based AI method named IDx-DR was used to assess two colour fundus pictures (45°) for each eye. Two retina experts performed UWF colour fundus imaging and assigned an International Clinical DR severity score to the images based on both 7-field area projection (7F-mask) grading and total gradable area (UWF full-field).
According to the findings of the research, when compared to UWF imaging analyzed by human specialists, the autonomous AI-based DR evaluation displayed significant accuracy in detecting asymptomatic non-proliferative diabetic individuals with referable DR.
The researchers discovered that the autonomously AI-based approach and 7F-mask gradings equalled in 66.6 percent of cases, while the autonomous AI-based method and UWF full-field gradings were identical in 66.7 percent of cases. They also proved that the sensitivity/specificity of the autonomous AI-based system was 100 percent against the 7F-mask grading and 95 percent against the UWF full-field grading.
Diabetic retinopathy is a frequent diabetic microvascular problem. According to the International Diabetes Federation, there are an estimated 537 million individuals worldwide who have diabetes, a figure that is expected to rise to 783 million by 2045.
Read all the Latest Lifestyle News and Breaking News here

















Comments
0 comment