
views
Water, the most abundant resource on Earth, covers nearly three-quarters of the planet’s surface and is vital for sustaining life. However, the majority of this water is saline and unsuitable for drinking or agricultural use. As a result, reliance on groundwater extraction has intensified, raising concerns about its depletion and the looming threat of water scarcity.
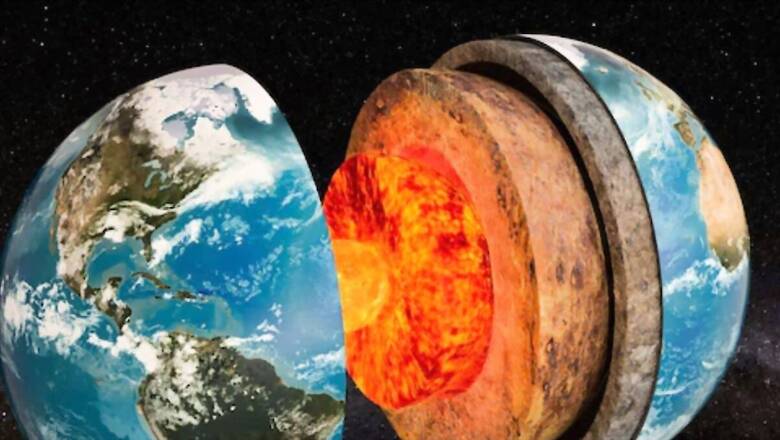
Research conducted in 2021 by scientists from the University of Saskatchewan, as reported by Live Science, shed light on the distribution of Earth’s water resources. While the ocean remains the largest reservoir, containing approximately 132 cubic miles of water, groundwater reservoirs are significantly smaller, comprising only around 43.9 cubic kilometres, approximately a quarter of the total water on Earth. Notably, much of this groundwater is potable, making it essential for human consumption and irrigation.
The process of groundwater replenishment, primarily through rainfall, is crucial for maintaining water levels. Despite the continuous extraction of groundwater, it is replenished annually, as documented in the journal Geophysical Research Letters. However, concerns about over-extraction persist, prompting calls for sustainable water management practices.
A report published in 2015 by the Nature Geoscience Journal highlighted the significance of deep groundwater reserves, revealing that approximately 22.6 cubic kilometres of water are stored within the Earth’s crust. Recent findings suggest a slight increase in this figure to 23.6 cubic kilometres, indicating the dynamic nature of groundwater reserves.
Grant Fresugon, speaking to Live Science, emphasised the potential of groundwater reservoirs for addressing water scarcity challenges. While acknowledging the salinity of deep groundwater as a limitation, he stressed that with further research, viable solutions could be developed to enhance water quality and availability.
In response to mounting concerns, calls for government intervention to curb the overuse of water resources through agricultural subsidies and industrial regulations have intensified. Addressing unsustainable practices and promoting conservation measures are essential steps towards mitigating water scarcity and ensuring equitable access to clean water for all.
While Earth’s water resources are vast, ensuring their sustainable management and equitable distribution is paramount. Through concerted efforts and scientific advancements, the global community can work towards securing a water-secure future for generations to come.


















Comments
0 comment