
views
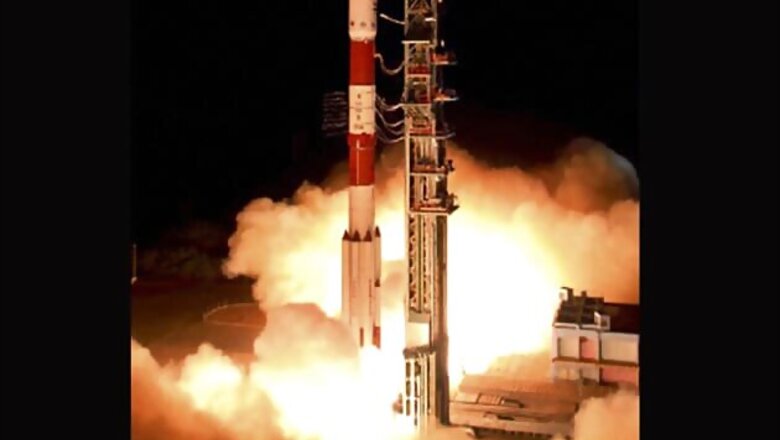
New Delhi: RISAT is the name of a series of radar imaging reconnaissance satellites, commonly called spy satellites, deployed in the space by India. Till now, India has two of these operational. The first one, named RISAT-2 was prioritised over RISAT-1 in the aftermath of the 2008 Mumbai terror attacks as the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) needed some time to develop its own synthetic aperture radar. It is not known how many satellites are planned in this series as officially ISRO says nothing about it.
The RISAT 1 is the heaviest earth observation Indian satellite in space and is the heaviest to be launched by a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV). It weighs near about 1850 kg.
So RISAT-2 which was placed in orbit on April 20, 2009, carried an Israel Aerospace Industries' X band synthetic aperture radar. However, the RISAT-1 launched on April 26, 2012, carried an ISRO-developed C band synthetic aperture radar.
What's unique?
Synthetic aperture radars, the main sensors of the RISAT series are immune to the vagaries of nature like rain, fog, smog or heavy cloud cover which previous Indian observation satellites, dependent on optical and spectral sensors, could not see through.
Both the C and the X band have true all weather, day and night monitoring capability throughout their lifespan.
Uses:
Though the Indian media went gaga, calling it India's eye in the sky, ISRO's decision to go for a C band radar suggests that RISAT 1 will more likely be used for survey and mapping to aid natural resource management and to plan better disaster mitigation and response. It has reconnaissance capabilities but is not built as a dedicated spy satellite.
The X band radar of RISAT 2 which uses higher frequencies and thus ensure greater bouncebacks is however a dedicated eavesdropping satellite. The dedicated reconnaissance satellite can be used to keep an eye on India's porous borders, on sensitive targets in adversary countries and on the movement of ships on the high seas.
Future satellites:
ISRO is working on ASTROSAT, GSAT series and the IRNSS series, the last two being part of the GAGAN and the IRNSS projects, i.e the Indian equivalent of the American GPS or Russian GLONASS systems.


















Comments
0 comment