
views
Repairing the File

Make sure that you're using a Windows computer. You can only repair an Excel file in the Windows version of Excel. If you're using a Mac, try one of the other methods in this article.
Open Excel. Its app icon resembles a green box with a white "X" on it.
Click Open Other Workbooks. This option is next to a folder-shaped icon in the lower-left corner of the window.
Click Browse. It's a folder-shaped icon in the middle of the page. Doing so opens a File Explorer window.
Select your Excel file. Go to the folder in which your corrupted Excel file is stored, then click the Excel file to select it.
Click the "Menu" icon Android 7 Dropdown. It's the downward-facing arrow to the right of the Open button. A drop-down menu will appear.
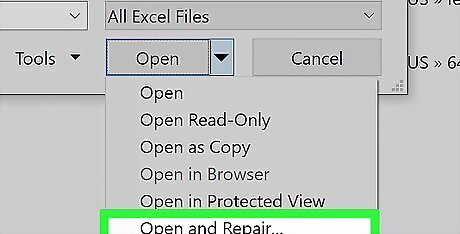
Click Open and Repair…. This option is at the bottom of the drop-down menu. If Open and Repair... is greyed out, make sure that your Excel file is selected and try again. If it's still greyed out, you can't repair this file.
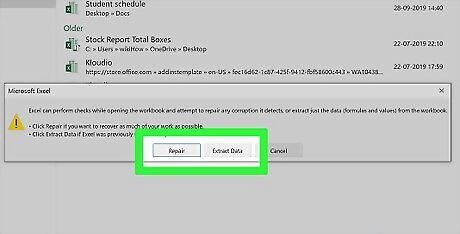
Click Repair when prompted. It's in a pop-up window. Windows will begin attempting to repair your file. If you don't have this option, click Extract Data instead, then click either Convert to Values or Recover Formulas. This will recover any salvageable data.
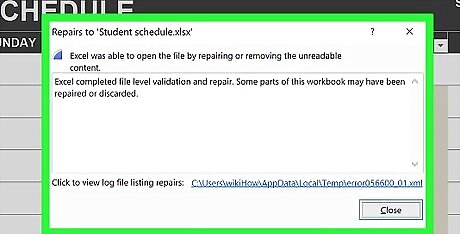
Wait for the file to open. This may take a few minutes if your Excel file is large. If the file still won't open, go back through this process and click Extract Data instead of Repair when prompted.
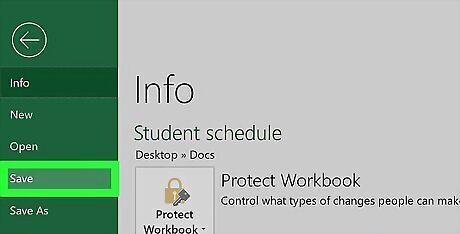
Save your file. Once the repaired file opens, press Ctrl+S, double-click This PC, select a save location, enter a file name, and click Save. Be sure to select a different file name than the one which you used for the corrupted Excel file.
Changing the File Type on Windows
Understand why the file type matters. Sometimes, Excel documents created on older computers or versions of Excel become unstable on newer versions; similarly, Excel documents can be saved in many different file formats. By changing the Excel file format to "xlsx" (or "xls" for older programs), you can fix this problem.
Open Start Windows Start. Click the Windows logo in the bottom-left corner of the screen.
Open File Explorer Windows Start Explorer. Click the folder-shaped icon in the lower-left side of the Start window.
Click the View tab. It's at the top of the File Explorer window. A toolbar will appear below this tab.
Check the "File name extensions" box. This option is in the "Show/hide" section of the toolbar. Doing so will allow you to see the file type extensions at the end of files, including your Excel document.
Select your Excel file. Go to the location of the Excel document that you want to recover, then click the document to select it.
Click Home. It's a tab in the upper-left side of the File Explorer window. This will prompt a toolbar to appear.
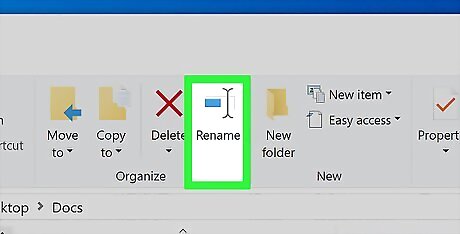
Click Rename. This option is in the "Organize" section of the toolbar. Clicking Rename will cause the Excel file's name to become highlighted.
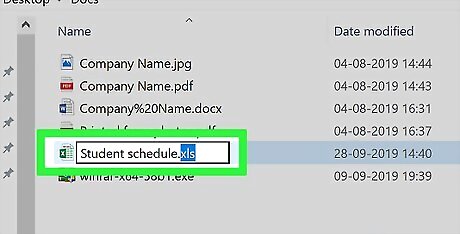
Change the file type. Replace whatever comes after the period at the end of the file name with xlsx and then press ↵ Enter. For example, if the document was named "Spreadsheet1.docx", you would change it to "Spreadsheet1.xlsx". If the file extension already is "xlsx", try using "xls" or "html".
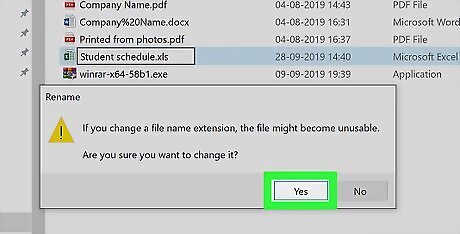
Click Yes when prompted. This will confirm your changes and change the file extension.
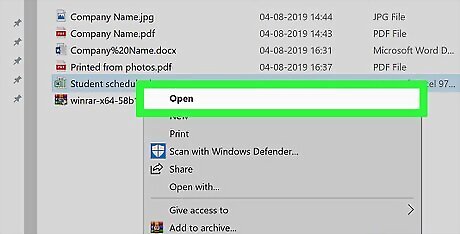
Try opening the file. Double-click the file to open it. If the file opens in Excel (or, if you selected "html" as the extension, a web browser), your file has successfully been recovered. If you chose the "html" extension, you can convert the webpage into an Excel document by dragging the html file onto the Excel icon and then saving the file that opens as a new "xlsx" file. If the file still won't open, proceed to the next Windows method.
Changing the File Type on Mac
Understand why the file type matters. Sometimes, Excel documents created on older computers or versions of Excel become unstable on newer versions; similarly, Excel documents can be saved in many different file formats. By changing the Excel file format to "xlsx" (or "xls" for older programs), you can fix this problem.
Open Finder. Click the blue, face-shaped app icon in your Mac's Dock.
Select the Excel file. Go to the folder in which your Excel file is located, then click the Excel file that you want to recover.
Click File. This menu item is in the top-left corner of your Mac's screen. Clicking it prompts a drop-down menu.
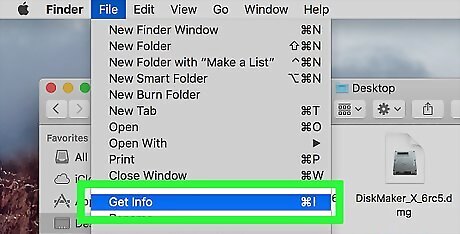
Click Get Info. It's in the File drop-down menu. This will open a pop-up window.
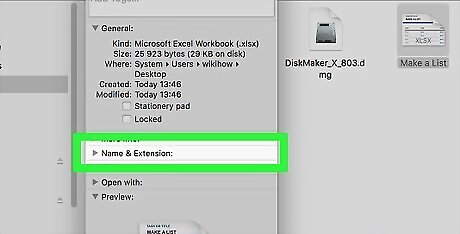
Expand the "Name & Extension" section if necessary. If you don't see any file name or extension below this category, click the triangle to the left of the "Name & Extension" heading to view the file's name and extension.
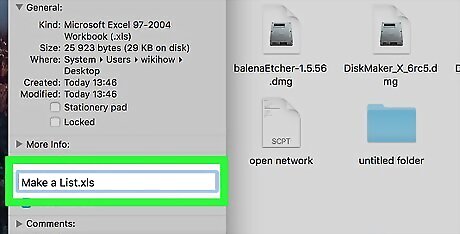
Change the file type. Replace whatever comes after the period at the end of the file name with xlsx and then press ⏎ Return. For example, if the document was named "Spreadsheet1.txt", you would change it to "Spreadsheet1.xlsx". If the file extension already is "xlsx", try using "xls" or "html".
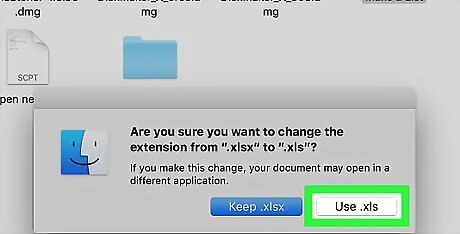
Click Use .xlsx when prompted. This will confirm your decision and change the file type.
Try opening the file. Double-click the file to open it. If the file opens in Excel (or, if you selected "html" as the extension, a web browser), your file has successfully been recovered. If you chose the "html" extension, you can convert the webpage into an Excel document by dragging the html file onto the Excel icon and then saving the file that opens as a new "xlsx" file. If the file still won't open, proceed to the next Mac method.
Recovering a Temporary Save on Windows
Understand the limitations of this method. Like most Microsoft Office products, Excel will automatically save recovery versions of files, meaning that you may be able to restore a partial version of your corrupted Excel document. However, Excel doesn't always save these files in time, and you most likely won't be able to recover the whole document in this way.
Open Start Windows Start. Click the Windows logo in the bottom-left corner of the screen.
Type in this pc. This will search your computer for the "This PC" program.
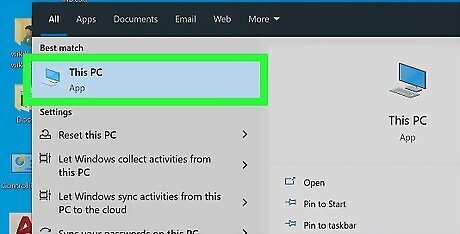
Click This PC. It's the computer monitor-shaped icon at the top of the Start window. Doing so opens the This PC window.
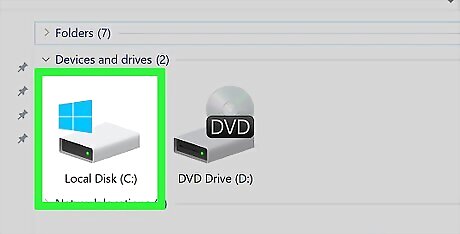
Double-click your computer's hard drive. This is usually the "OS (C:)" option below the "Devices and drives" heading in the middle of the page.
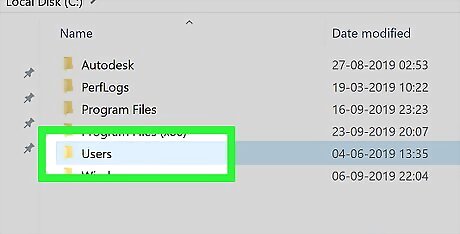
Double-click the "Users" folder. You'll find this in the middle of the hard drive's folder.
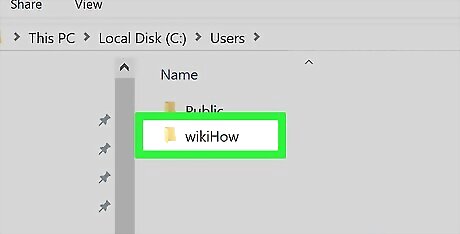
Double-click your user folder. This folder is labeled with part or all of your username on your computer.
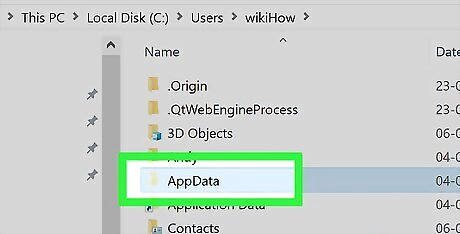
Double-click the "AppData" folder. It's in the "A" section, so you'll most likely find this folder near the top of the window. If you can't find this folder, click the View tab, then check the "Hidden items" box in the "Show/hide" section to prompt the "AppData" folder to appear.
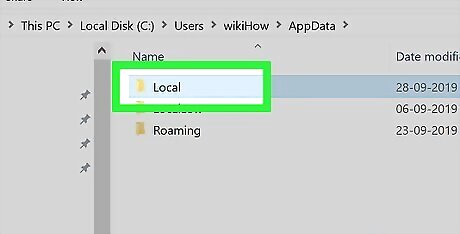
Double-click the "Local" folder. This option is near the top of the folder.
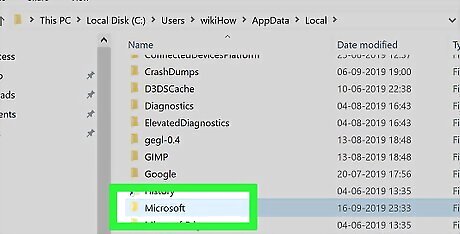
Scroll down and double-click the "Microsoft" folder. You'll find it in the "M" section.
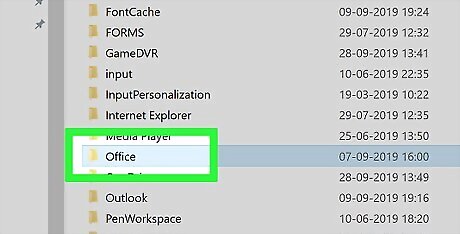
Double-click the "Office" folder. It's in the "O" section of the Microsoft folder.
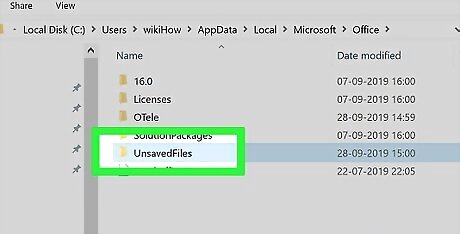
Double-click the "UnsavedFiles" folder. This folder should be near the top of the window.
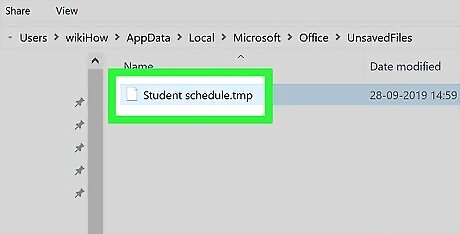
Select an Excel file. Look for an Excel file icon that has a name matching your corrupted Excel file, then click it to select it. If you don't see any files here, a recovery version of your Excel document was not saved.
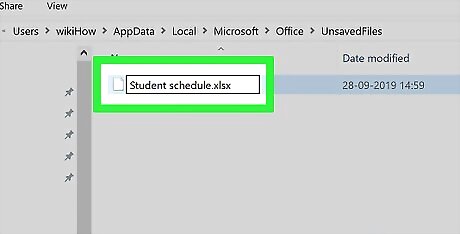
Change the Excel file's extension. To do so: Click View Check the "File name extensions" box. Click Home Click Rename Replace the .tmp section with .xlsx Press ↵ Enter. Click Yes when prompted.
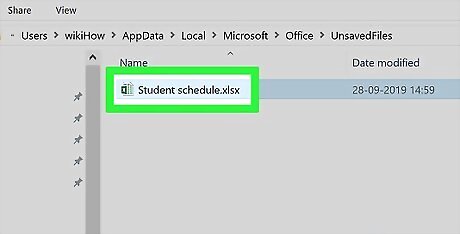
Open the Excel file. Double-click the file that you just renamed to open it.
Save your file. Once the restored file opens, press Ctrl+S, double-click This PC, select a save location, enter a file name, and click Save. Be sure to select a different file name than the one which you used for the corrupted Excel file.
Recovering a Temporary Save on Mac
Understand the limitations of this method. Like most Microsoft Office products, Excel will automatically save recovery versions of files, meaning that you may be able to restore a partial version of your corrupted Excel document. However, Excel doesn't always save these files in time, and you most likely won't be able to recover the whole document in this way.
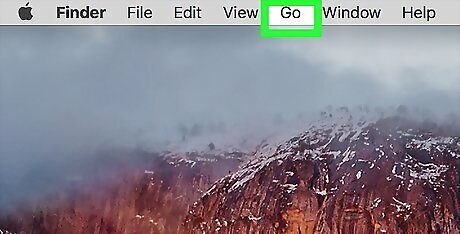
Click Go. This menu item is at the top of the screen. Clicking it prompts a drop-down menu. If you don't see the Go menu item, first open Finder or click the desktop to make it appear.

Hold down the ⌥ Option key. After doing this, you should see the Library folder appear in the Go drop-down menu.
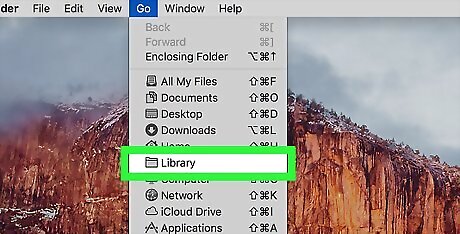
Click Library. It's in the Go drop-down menu. This will open the Library hidden folder.
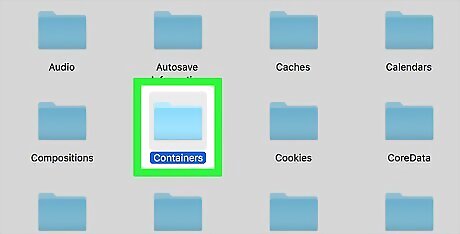
Open the "Containers" folder. Double-click the "Containers" folder, which is in the "C" section of the Library folder.
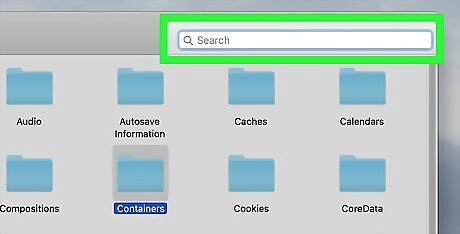
Click the search bar. It's in the upper-right side of the window.
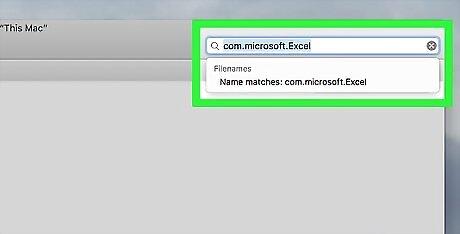
Search for the Microsoft Excel folder. Type in com.microsoft.Excel and press ⏎ Return.
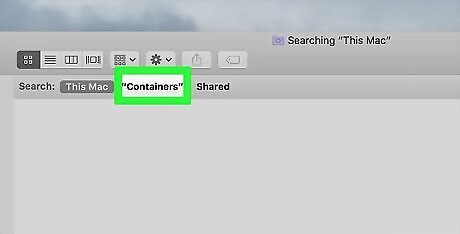
Click the Containers tab. You'll find this to the right of the "Search:" heading near the top of the Finder window.
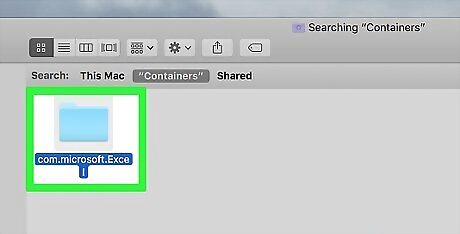
Open the "com.microsoft.Excel" folder. Double-click this folder to open it.
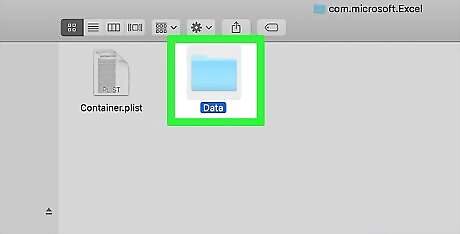
Open the "Data" folder.
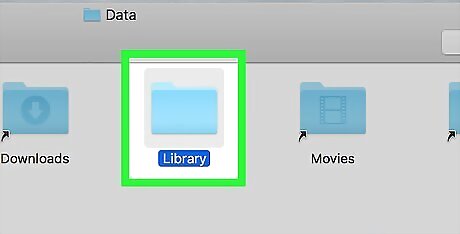
Open the "Library" folder.
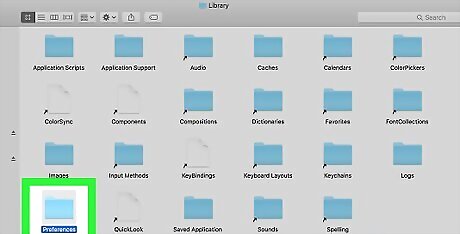
Open the "Preferences" folder. If you don't see this folder, scroll down to find it.
Open the "AutoRecovery" folder. This will bring up a list of automatically saved versions of your Excel files.
Find a temporary version of your Excel file. The temporary version of your Excel file should have some or all of the file's name in its title. If you can't find the temporary version of your Excel file, it wasn't backed up.
Select the Excel file. Click the Excel file to do so.
Click File. It's a menu item in the upper-left corner of your Mac's screen. A drop-down menu will appear.
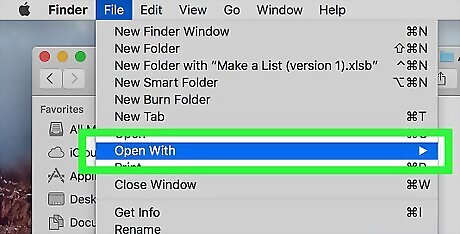
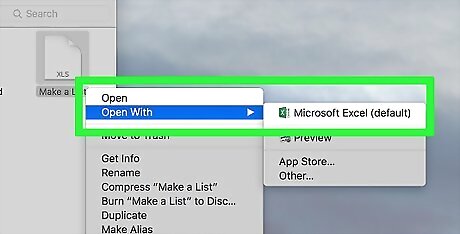
Select Open With. This option is near the top of the File drop-down menu. You should see a pop-out menu open.
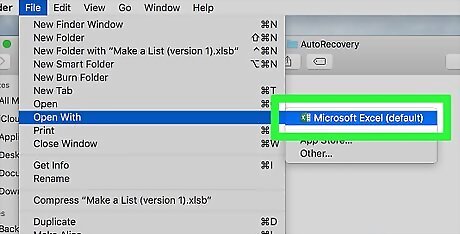
Click Excel. It's in the pop-out menu. Doing so will prompt the temporary version of the Excel document to open in Excel. The temporary version will probably not include some of your most recent changes to the original Excel document.
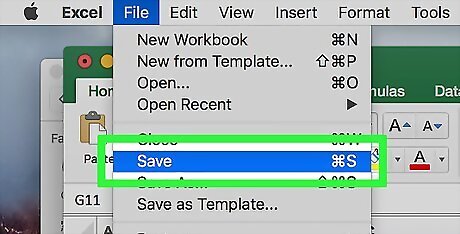
Save the document. Press ⌘ Command+S, then enter a file name, select a save location in the "Where" menu, and click Save.















Comments
0 comment