
views
Exercising Your Eyes

Cover your good eye with a patch to strengthen the other eye's muscles. If you notice that 1 eye is more affected than the other, cover the good eye with a patch and wear it for about 2 hours every day. This will force the muscles in the affected eye to work harder and become stronger over time. You'll need to do this for a few weeks before you may notice an improvement with your exotropia.Tip: If your child with exotropia doesn't like wearing a patch, get your child excited about the patch by letting them pick out a colorful patch with a fun pattern. If you only find white patches, let your child decorate the patch with their choice of stickers. If both of your eyes experience exotropia, alternate wearing the patch for a few hours a day so each eye is covered at some point.
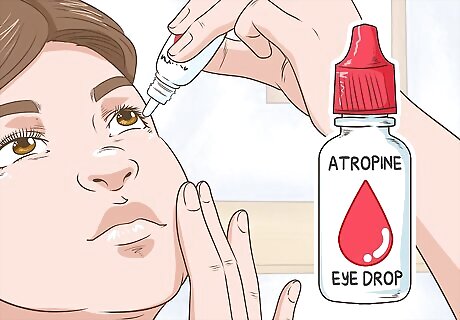
Use drops to blur the vision in 1 eye instead of using a patch. If you don't like wearing a patch to strengthen the affected eye, ask your doctor about using over-the-counter atropine drops. Follow your doctor's recommendations about how many drops to use. In general, you'll probably squirt 1 drop into the eye and it will blur your vision for about 4 hours. This will make your affected eye work harder while the vision in your stronger eye is blurred.
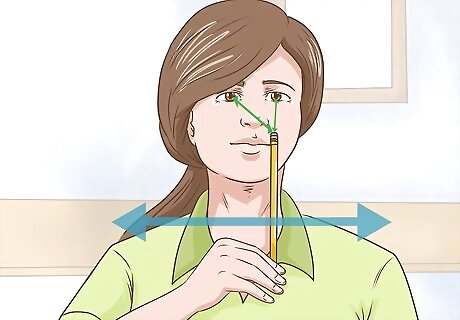
Do pencil pushups to practice focusing your eyes on a fixed point. To practice aligning your eyes, hold a pencil in front of you at arm's length and choose something on the pencil to focus both of your eyes on. For example, look at the eraser or a word on the side of the pencil. Then slowly bring the pencil towards your nose while you continue to focus on the fixed point. Focus until it looks blurry. You can do this exercise as often as you like throughout the day.
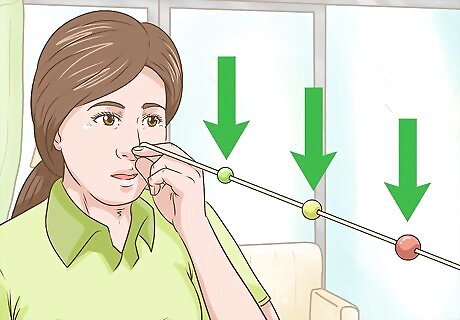
Try the brock string exercise to improve eye coordination and focus. Tie a 5 ft (1.5 m) string to a chair or rail and slide three beads that are about 1 inch (2.5 cm) in size onto the string so they're at least 1 foot (30 cm) apart. Then hold the other end of the string near your nose so the string is taut. Focus on 1 bead at a time so it looks like it's at an intersection of two strings. Use different colored beads so your eyes can tell which bead you're focusing on. If you see the X shape in the strings before or after the bead you're focusing on, practice focusing both of your eyes onto the bead.
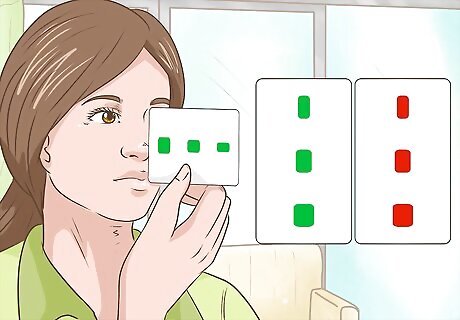
Improve your focus by staring at different sized barrels. Draw 3 red barrels on a 3 in × 5 in (7.6 cm × 12.7 cm) card and 3 green barrels on the back of the card so the barrels mirror each other. Make the barrels progressively bigger in size, so you have a small, medium, and large barrel on both sides of the card. Hold the card against the tip of your nose so it faces out lengthwise and turn the card so it acts like a dividing wall between your eyes. Then look at the largest barrel that's farthest from your nose and try to focus so the green and red barrels appear as 1. Try to hold your focus for about 5 seconds before moving on to another barrel. Repeat this exercise again while focusing on the middle and then smallest barrels.
Getting Medical Attention
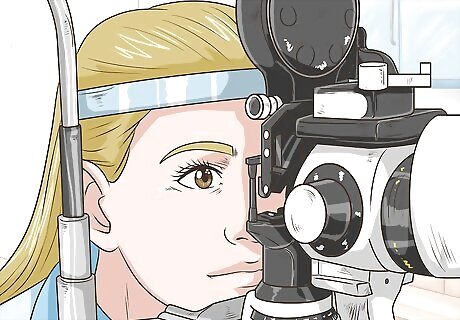
Get your eyes examined by an ophthalmologist. The specialist will take your family medical history and evaluate your vision. In addition to asking about your symptoms, they'll check the structure of your eyes, test how your eyes focus, and evaluate your eyesight. If your optometrist specializes in eye issues, you could have them examine your eyes for exotropia. An optometrist is an eye doctor who can examine eyes and prescribe eyeglasses or contact lenses. An ophthalmologist is a medical doctor who can diagnose eye conditions, perform surgery, and provide vision therapy.

Attend vision therapy every week to strengthen your eye muscles. Ask your ophthalmologist to develop a personalized therapy plan for you and work every week at retraining your eye-brain connections. The doctor will use computer devices and tools, such as therapeutic lenses, prisms, and filters to retrain your nervous system. Because vision therapy is unique to each person, your doctor will develop a special therapy plan for you that includes a mixture of these treatments. As with any therapy, you'll need to have regular visits over several weeks before you may notice an improvement with your eyes.
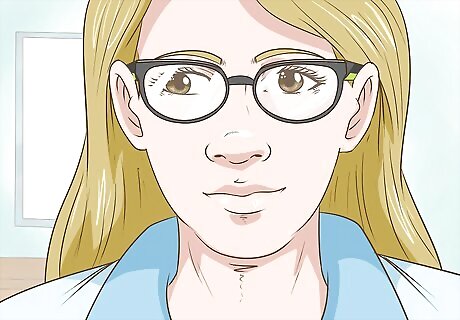
Get glasses or contacts to treat other vision issues. If your eye doctor determines that you're near or farsighted, they'll prescribe corrective lenses or glasses. Sometimes wearing glasses or contacts to improve your vision will help you keep your eyes aligned and reduce the frequency of exotropia. If you already have wear glasses, ensure that the prescription is recent. If it's been more than 1 year since you updated, schedule an eye exam.
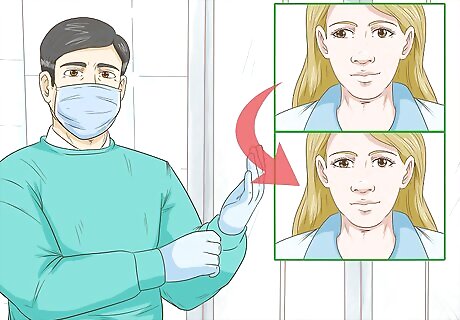
Find out if you're a good candidate for surgery to correct your exotropia. Researchers are still studying whether eye surgery can correct exotropia or if it's more of a cosmetic procedure. Discuss this option with your ophthalmologist to determine if you think you would benefit from surgery. If you do choose surgery, the doctor will cut the muscles that move the eye from side to side. Then they'll shorten the muscles and stitch them in place to keep the eyes aligned in the center.Did You Know? Researchers are also studying whether it's better to get surgery as a child or wait until adulthood. This is another reason why it's important to talk with your doctor about surgery outcomes. Eye surgery is usually an outpatient procedure and you'll recover quickly. Keep in mind that people who undergo surgery for exotropia often require repeated surgeries.




















Comments
0 comment