
views
Understand the Difference Between Stress and Strain
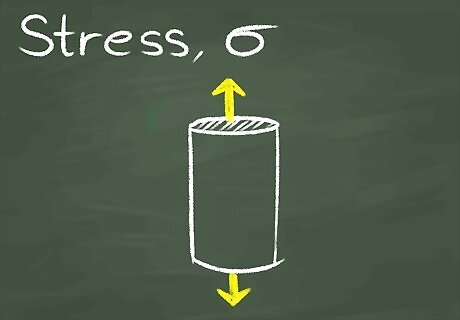
Note that material stress is caused by axial stretching force. For example, pulling straight out on a piece of taffy will stretch the taffy due to applied stress.
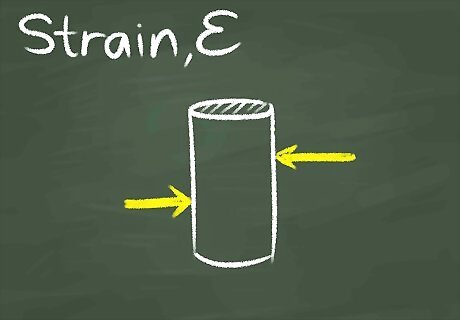
Understand that material strain is caused by shearing force perpendicular to the axis of the material. For example, pushing on the middle of a tennis racket string will bend the string due to applied strain.
Perform the Calculations

Calculate the bulk modulus. Bulk modulus expresses the strength of the material when external force is applied in the axial direction, producing stress. The external pressure p (force times area over which the force is applied, expressed in MPa) applied to the material equals the dilation (a unitless number) times the bulk modulus K (expressed in MPa). As p = K times dSs, the bulk modulus K is determined as p divided by dSs.

Figure out the shear modulus. Shear modulus expresses the strength of the material when external force is applied in the perpendicular direction, producing strain. The external pressure p (force times area over which the force is applied, expressed in MPa) applied to the material equals the dilation (a unitless number) times the shear modulus G (expressed in MPa). As p = G times dSn, the bulk modulus G is determined as p divided by dSn.

Determine the Young's Modulus. Stressing a material will cause a proportional strain and vice versa. Young's modulus describes the relationship between stress and strain in the material. It is a linear relationship up to the yield point of the material. Young's modulus E equals stress divided by strain.














Comments
0 comment