
views
In these times, when the phone has become the primary tool to stay connected, it gets a little annoying when it is marred by weak signals and poor reception - leaving us with either incomprehensible speech, call drops or simply, no network.
As there are no prior alerts as to where we might lose connection, we are usually unprepared for it. Many of the times, we manage to get connected again in a few attempts, but there are also occasions, when the phone cannot connect to the network. Such situations get worse in dead zones when there is an emergency phone call to make or an important message to receive.
Preparing you for such situations, we bring you 5 simple tricks that can help you find better signal when stuck in areas with low connectivity.
1. Switch from 3G to 2G: If you continue to experience low signal strength in a particular area, you can boost signal on your phone by switching from 3G to 2G. It may, however, consequently lead to a lag in the Internet speed, but you, in all likelihood, will have signal strengthened to makes calls and send messages. “Switching to 2G can allow users to get better voice signal as long as operators’ 2G coverage in that area is better than 3G coverage. Do remember that most often 2G is propagated over a lower frequency band than 3G and has a more widespread network (in most cities) than 3G, hence the likelihood of getting better signal for voice (driven by better coverage) on 2G (as compared to 3G) is quite high,” explains Rohan Dhamija, partner, head - India & South Asia, Analysys Mason.
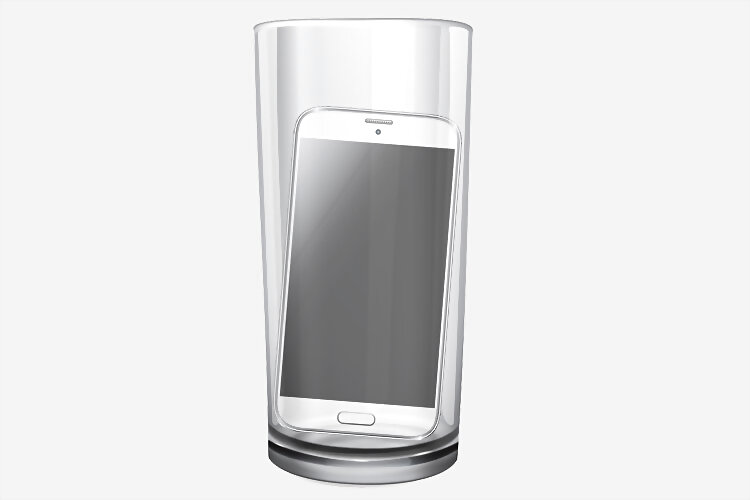
2. Glass tumbler: This off-beat yet useful remedy can help improve your phone’s reception in low or say, no connectivity areas. In case you get caught in areas where the signal on your phone is almost negligible, we advise you to look for a glass tumbler. Just put your phone in the tumbler and you are likely to find some signal on your phone. This is a tried and tested ‘jugaad’. If not much, you would get signal enough to make at least a phone call. Wondering how would you talk with your phone in a tumbler? Use your earphones or put it on loudspeaker.

3. Install boosters: Many of us are unable to properly connect to the network in daily environments such as office or home. It so happens because of materials like reinforced concrete and wire mesh used in the construction of the building. Cell phone signals, therefore, cannot easily pass through the walls of such buildings - leading to weak signals or connection loss. What comes to rescue here is a booster that can amplify cell phone signal and retransmit it to areas that receive little or no signal. While installing the signal booster, choose a place carefully as it should be placed in an area that receives good signal. This may not upgrade you to a flawless powerful network, but you are likely to have an improved connection.
4. Change the way you hold your phone: Remember “Antennagate” that happened to Apple after the iPhone 4 launch and users complained of the poor reception in the phone? It was later observed that there was a reception drop on holding the phone tightly or across a particular point. It was because gripping the phone tightly added another layer and made it difficult for the phone to send and receive signal. Though this issue might not hold true for all phones, but it is suggested that better signal can be received by gripping the phone lightly so that the antenna inside doesn’t get blocked.
5. Forward all calls to another number: If your phone fails to receive proper signal in a particular place, we suggest you to forward your calls to another number that works fine in the same environment. Also, you can consider forwarding your calls to your landline.
There’s is also a myth that users should switch to WiFi in areas where it’s available and turn off mobile data to free up the mobile network for calls. But this, technically, doesn't add to better signal strength. Though it may contribute to a little faster data download for other users.
“A data user that falls back on WiFi when it is available will free up network capacity for other users that do not have WiFi to fall back on. This frees up the network (from a capacity perspective) and hence, allows users, which do not have WiFi, to get better user experience (not in terms of the signal strength that you see, but rather the speed that you get for data download),” says Dhamija.
So, this is less an issue related to signal strength (as signal strength is driven by coverage) and more an issue related to better user experience / data download speed (which is driven by available capacity on the network).
With instant messaging and Internet calls (VoIP) available through services like Skype, WhatsApp, Viber, there is an easy alternative available in case your cellular network is out of coverage area. But that requires you to be connected to a WiFi network.














Comments
0 comment