
views
A year and a half after the Coronavirus pandemic wrecked our collective lives, our society has been grappling with fear and insecurity. As a result, we have seen misinformation spread like wildfire, and many resorting to bizarre and incorrect methods of dealing with the virus. With this column, which will be published every Sunday, we aim to address any health or vaccine-related question our readers might have about the coronavirus pandemic.
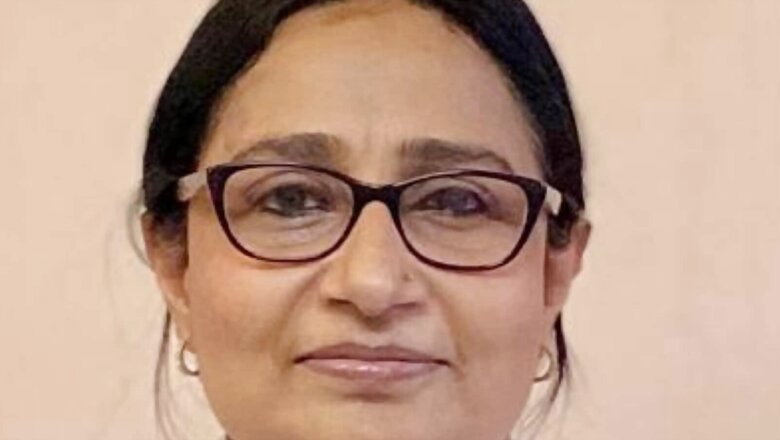
In this week’s column, Dr. Sumitra Bachani, Fetal Medicine Specialist, Nodal officer for COVID19, Associate Professor, Gynecologist, and Obstetrician Department, Safdarjung Hospital and Vardhman Mahavir Medical College, talks about neonatal health and how COVID-19 positive new mothers should interact with their infants.
Does pregnancy increase the need for critical care in the setting of COVID-19 infection?
Most pregnant women with COVID 19 may have asymptomatic or mild disease. Compared with pregnant women without COVID-19, those with symptomatic COVID19 are at increased risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes, including admissions to the ICUs, iatrogenic preterm birth, pregnancy-associated hypertension-like symptoms, operative intervention, and death.
Does COVID-19 present an increased risk of severe morbidity and mortality for pregnant and recently pregnant women compared with non-pregnant women?
Pregnant women with certain high-risk conditions have a greater risk of severe illness from COVID-19 such as pre-existing medical conditions (Hypertension, Diabetes), chronic respiratory conditions (COPD, Asthma, Cystic Fibrosis), Homozygous sickle cell disease. There are also adverse effects on recipients of immunosuppression therapies (enough to significantly increase risk of infection), Dialysis, or anyone under treatment for advanced/chronic kidney disease, congenital or acquired heart disease, or organ transplant.
What is the effect of COVID-19 on fetal and neonatal outcomes?
Whether COVID 19 can be transmitted to the fetus during pregnancy is being researched. To date, most fetuses and neonates born to mothers with mild to moderate COVID 19 infection are seen to do well vis a vis the COVID 19 infection. However in pregnant women with severe to critical illness the fetus is at risk of perinatal morbidity (due to hypoxia as the mother is hypoxic), early preterm birth, and mortality.
How can doctors help their pregnant and postpartum patients manage stress, anxiety, and depression?
On each antenatal visit, the pregnant woman is asked about any feelings, thoughts, or symptoms concerning stress, anxiety, or depression. In case she is found to be suffering from any of these, she is provided non-directive counseling and her fears are allayed. She is also provided with psychologist/psychiatrist services as per the need concerning her mental condition.
How should thromboprophylaxis be managed for pregnant and postpartum patients with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 infection?
There are established guidelines of various societies of OBGYN/FOGSI which are followed.
Should monoclonal antibodies be used as a treatment option for pregnant patients?
Currently, this is also under research.
Is there any benefit associated with the use of corticosteroid treatment for pregnant patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 illness?
Yes, it’s beneficial and administered as per established protocols.
How should a mother-infant interact when the mother has suspected or confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection?
Mother and infant can stay together in the same room if the mother is not critical or has severe COVID 19 which needs hospitalization. If they are roomed together, the infant can be taken care of by the mother and another family member should assist her. The infant’s crib can be kept at a distance of 6 feet from the mother during her active infection and the infant can be brought to her for breastfeeding. Prior to handling the infant or while breastfeeding the mother should wash her hands and wear a mask. It’s important to note that infants should not be made to wear a mask. Once the mother is non-infectious she can keep the baby with herself at all times.
Do you see any post covid effect in pregnant women?
Yes, it’s the same as post covid sequelae in non-pregnant or as in the general population.
How important is the covid vaccine for pregnant women and young mothers? Why?
Compared to pregnant women without COVID-19, those with symptomatic COVID-19 are at increased risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes, including admissions to the ICUs, iatrogenic preterm birth, hypertension and associated complications, operative intervention, and in some extreme cases even death. Additionally, the fetus is at risk of perinatal morbidity (hypoxia) and mortality. Experts are of the view that the benefits of vaccination are far more than the risk of morbidity and mortality associated with COVID-19, especially if contracted during pregnancy. It is also being established that the mother may also pass the antibodies to the unborn fetus or in breast milk to her neonate.
In what conditions a mother should not take the vaccine?
As for the general population, pregnant women should avoid vaccination in the following conditions: If she has had anaphylactic or allergic reaction to the previous dose of COVID-19 vaccine and/or anaphylaxis or allergic reaction to vaccines or injectable therapies, pharmaceutical products, food-items etc.
Read all the Latest Lifestyle News here


















Comments
0 comment