views
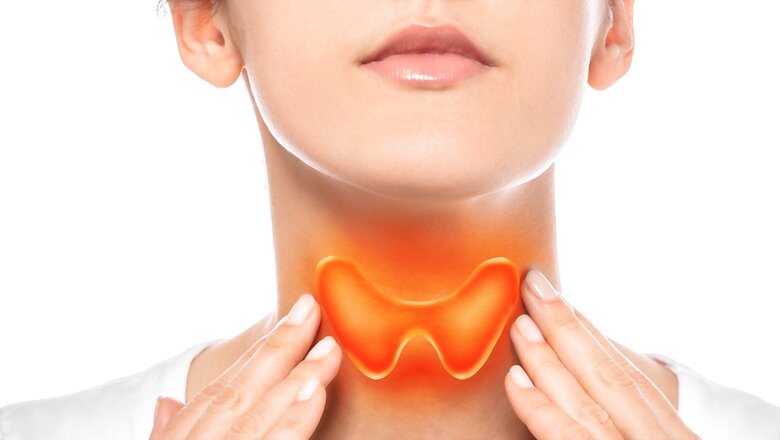
We frequently overlook thyroid difficulties and abnormalities in the midst of mounting worries about cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and other chronic diseases. Thyroid is a tiny but strong gland that plays an important role in our physical and mental health. This butterfly-shaped gland found under Adam’s apple stimulates the releases of hormones that go to all body organs and cells, influencing functions like respiration, heart rate, metabolism, mood, and body temperature.
Thyroxine, often known as T4, and triiodothyronine, or T3, are the two hormones secreted by the thyroid. When the thyroid isn’t operating correctly, it might have major health consequences.
Types of thyroid disease
Thyroid disease is classified into two types: hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.
An overactive thyroid, also known as hyperthyroidism, is frequently caused by Grave’s disease, an autoimmune illness in which the body creates excessive amounts of T3/T4. You can feel your heart beating, you’re losing weight or finding it difficult to gain weight, and you’re losing hair. You have the impression that your body is always in motion. Anxiety might arise as a result of this.
An underactive thyroid, commonly known as hypothyroidism (which is frequently caused by Hashimoto’s disease), indicates that the thyroid isn’t making enough hormone. Your body feels slowed down, you may gain weight, become chilly, and your nails may become brittle. When you think about it, it’s almost as if your body is slowing down. Furthermore, women may experience menstrual irregularity (excessive menstrual bleeding) and infertility, while children may experience poor development and delayed puberty.
Other thyroid issues
Thyroid nodules
Thyroid nodules are benign growths on the thyroid that do not generate hormones. This is generally identified by palpation followed by an ultrasound. The vast majority are benign, however, up to 10% may be malignant.
Thyroid cancer
Although this is not a thyroid “disease,” it is possible to get thyroid cancer. Thyroid cancer is normally detected when there is a significant development on the thyroid, which may look like a hump on the neck. Most thyroid cancers are random and not inherited. Although there is no yearly screening for thyroid cancer. If you find a lump on your neck that does not go away, get medical treatment for a diagnosis.
What is the diagnosis procedure and treatment of thyroid disorders?
Blood tests are used to identify hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. A blood panel is requested to assess your thyroid hormone levels as well as antibodies that assault your thyroid gland.
If your thyroid gland produces less or excessive thyroid hormone, medication might be administered to either supplement or decrease the quantity of hormones in your bloodstream. Surgery or radioiodine treatments are more lasting therapies for hyperactive thyroids.
However, thyroid nodules are assessed with a specialised thyroid ultrasound, which is followed by a biopsy if the nodule is big and/or worrisome. If the thyroid biopsy results are worrisome or suggestive of malignancy, surgery is usually required. Treatment options for big benign nodules that are symptomatic (problems swallowing or breathing) include surgery or radiofrequency ablation of the lesion.
Read all the Latest Lifestyle News here















Comments
0 comment