
views
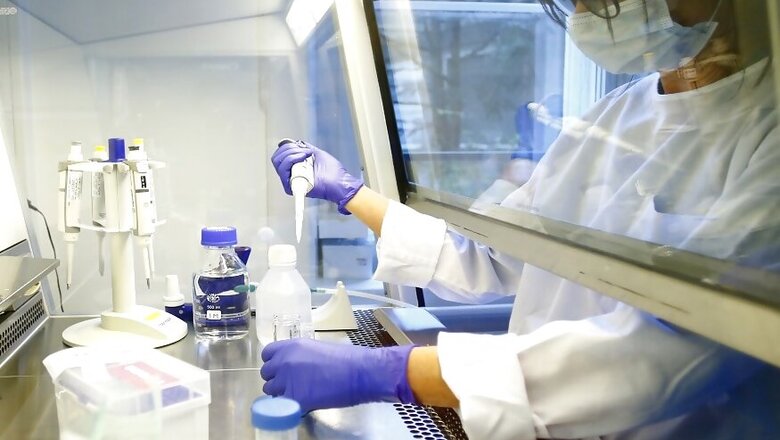
New Delhi: Researchers from the University of Oxford have said that Dexamethasone, a low-cost steroid is improving survival chances of Covid-19 patients. These were the results from a randomized trial and a detailed paper will be published on it soon. News18 explains how this drug works and the trial being carried out to test its efficacy.
What is Dexamethasone?
It is a low-cost steroid that is available widely, including in India. It is known to be used to treat inflammations and conditions such as arthritis, blood disorders, lupus, allergic reactions and skin conditions. India has not officially recommended its use so far.
Was the drug tested as part of a large trial?
Yes. Globally, doctors are using repurposed drugs as a line of treatment for Covid-19 patients. These are drugs that are already in use to treat other diseases. Scientists across the world are also carrying out trials on such drugs to test their efficacy among Covid-19 patients. One such trial – Randomised Evaluation of Covid-19 therapy trial (RECOVERY) was established in March 2020 and it is underway to test potential treatments for Covid-19.
As part of the Dexamethasone trial, a total of 2104 patients were randomized to receive 6mg of the drug once per day (either by mouth or by intravenous injection) for ten days and were compared with 4321 patients randomized to usual care alone, a news release issued by University of Oxford said.
What are the results of the trial?
The drug cut deaths by a third in patients on a ventilator and by a fifth in patients receiving only oxygen. There was no benefit among patients who did not require respiratory support. “Based on these results, 1 death would be prevented by treatment of around 8 ventilated patients or around 25 patients requiring oxygen alone,” the University’s release said.
“Overall, dexamethasone reduced the 28-day mortality rate by 17% with a highly significant trend showing greatest benefit among those patients requiring ventilation. But it is important to recognize that we found no evidence of benefit for patients who did not require oxygen and we did not study patients outside the hospital setting,” the release added.
What have researchers involved in the trial said on the results?
Peter Horby, Professor of Emerging Infectious Diseases in the Nuffield Department of Medicine, University of Oxford, and one of the Chief Investigators for the trial, said, “Dexamethasone is the first drug to be shown to improve survival in COVID-19. This is an extremely welcome result. The survival benefit is clear and large in those patients who are sick enough to require oxygen treatment, so dexamethasone should now become standard of care in these patients.
Dexamethasone is inexpensive, on the shelf, and can be used immediately to save lives worldwide.
Martin Landray, one of the lead researchers, said, “These preliminary results from the RECOVERY trial are very clear –dexamethasone reduces the risk of death among patients with severe respiratory complications. COVID-19 is a global disease –it is fantastic that the first treatment demonstrated to reduce mortality is one that is instantly available and affordable worldwide.”
Which other drugs being tested as part of the recovery trial?
Over 11,500 patients have been enrolled from over 175 National Health Service hospitals in the United Kingdom for different trials. Other drugs being tested are – Lopinavir-Ritonavir (used to treat HIV), low-dose Dexamethasone, Hydroxychloroquine (trial stopped due to lack of efficacy), Azithromycin (a common antibiotic) and Tocilizumab (an anti-inflammatory treatment given by injection).

















Comments
0 comment