
views
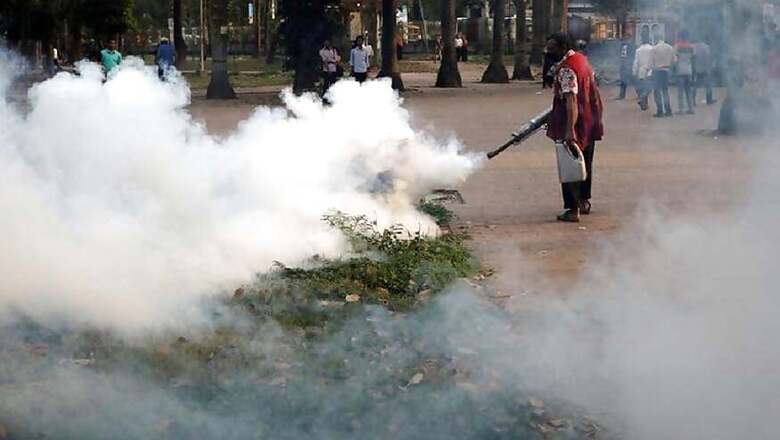
The mosquito-borne diseases are creating havoc in across a number of countries, especially those lying in the Asian and African sub-continent. These diseases include malaria, chikungunya, dengue, zika and encephalitis, all spread by the vector mosquitoes. While the mosquitoes can bite and infect at any time of the year, the numbers are usually high during the monsoon season, as water collected during this time acts as a breeding ground for these mosquitoes.
While Asian nations like Taiwan, Thailand, Myanmar and India have been reported to suffer a significant number of dengue, malaria and zika cases, African nations are also under the effect of these mosquito-borne diseases. Recently, there have been reports on the chikungunya outbreak in Ethiopia. The health ministry officials have now report the mosquito-borne disease outbreak has reached 20,000 cases.
As informed by the Ethiopia Public Health Institute (EPHI), the country has conducted an extensive anti-Chikungunya spray campaign in the disease’s epicenter, the eastern city of Dire Dawa. However, despite taking steps in the direction of dealing with the menace, there has been a spike in the number of Chikungunya sufferers. In addition to chikungunya, Ethiopia is also battling outbreaks of cholera, measles, and poliovirus.
Chikungunya is a viral disease, transmitted to humans by infected mosquitoes, specifically aedes mosquitoes. Mosquitoes become infected when they feed on a person already infected with the virus. Infected mosquitoes can then spread the virus to other people through bites.
The Chikungunya virus is most often spread to people by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes. These are the same mosquitoes that transmit dengue virus. They bite during the day and at night.
The infection can cause fever and severe joint pain, which is often debilitating. Other symptoms include muscle pain, headache, nausea, fatigue, and rash. The symptoms usually begin 3–7 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito.
The disease shares some clinical signs with dengue and Zika, and can be misdiagnosed in areas where they are common. As there is no cure, treatment is focused on relieving the symptoms.















Comments
0 comment