
views
Eat 5 servings of veggies every day.

Different veggies have different nutrients, so eat a variety. Veggies are extremely nutrient-dense and crucial for a healthy pregnancy. Fresh veggies have the most nutritional value, but frozen or canned veggies (with no added salt) are excellent, too! 1 standard serving of veggies = ½ cup (75 g). You really can’t go wrong with options, but good choices include: Broccoli Carrots Corn Tomatoes Legumes such as chickpeas, lentils, and soybeans Leafy greens like spinach, turnip greens, kale, and Swiss chard
Aim for 3-4 servings of lean meat a day.
Lean meats are rich in nutrients like protein, B vitamins, and iron. These nutrients are vital for your developing baby. Lean cuts of poultry, beef, pork, and goat are all great options, so go with what you like. A few things to keep in mind: 1 serving = 65 to 80g (depending on the meat). Cook the meats all the way through. Avoid rare and undercooked meats since they may contain dangerous bacteria like E. coli, Salmonella, and Toxoplasma gondii that could make you very ill. Heat/reheat hot dogs and deli meats until steaming (about 165 °F (74 °C))—even if the package says precooked. These meats may contain harmful bacteria called Listeria that could put you and your unborn baby at risk. Heating the meat properly kills the bacteria. If you’re vegan or vegetarian, be sure you’re getting enough protein from non-meat sources. You need to eat about 60 grams of protein a day. Also, remember to get your iron from other sources, such as beans and lentils. Wash cutting boards, dishes, and utensils that come in contact with raw meat thoroughly with hot, soapy water.
Consume 8 servings of whole grains daily.
Whole grains provide carbohydrates, fiber, and important nutrients. Breads, cereals, and pastas made with whole grain flour are your best options. Brown rice, whole grain corn, fortified cereals, and whole wheat tortillas are also great. Aim for 8 servings of whole grains a day. Serving sizes vary, but here are some common ones: 1 slice (40 g) of whole wheat bread ½ cup (75-120 g) of cooked rice, pasta, noodles, barley, buckwheat, or quinoa ½ cup (120 g) of cooked oatmeal 2/3 cup (30g) of wheat cereal flakes
Eat 2 ½ to 3 servings of dairy per day.

Milk, yogurt, and cheese are excellent sources of calcium. Calcium is one of the most crucial nutrients for pregnant people. Low-fat and skim dairy items are best because whole milk contains a lot of saturated fat (which pregnant people should limit or avoid). It’s perfectly fine to enjoy full-fat dairy occasionally, though; moderation is key! Alternatives, like soy milk, are a great substitute if you’re vegan/vegetarian or lactose-intolerant. Serving sizes vary, but here are some common ones: 1 serving of milk = 1 cup (240 ml) 1 serving of yogurt = 1 cup (245 g) 1 serving of shredded cheese = 1/3 cup (75 g) Soft cheeses like brie, Camembert, and ricotta are made with unpasteurized milk, so there's a risk of consuming harmful bacteria like Campylobacter, E. coli, Listeria, and Salmonella. These cheeses are safe to eat as long as they’re served hot and fully cooked.
Increase your protein intake with eggs.
You need to eat at least 60 grams of protein a day. Eggs are one of the best sources of protein out there (6 to 8 grams per egg). It’s important to cook eggs thoroughly and completely to avoid food borne illnesses and bacteria, though. A few other things to keep in mind when it comes to consuming eggs: 1 serving = 2 large eggs. Always buy eggs that are pasteurized. Unpasteurized eggs may contain harmful bacteria like E.coli, Salmonella, and Listeria that could make you and your unborn baby very sick. Avoid foods that contain raw or lightly cooked eggs like eggnog, cookie dough, homemade mayo, mousse, or meringue. Commercial mayo, dressings, and sauces containing pasteurized eggs are safe.
Aim for 2-4 servings of fruit every day.
Most fresh fruits are fiber-rich and full of essential nutrients. Fruits contain plenty of vitamin C and folic acid (both play an important role in fetal development). Constipation is a common problem for pregnant people, so the high fiber content in fresh fruit can really help keep things moving, so to speak. 1 serving of fruit is equal to: 1 medium apple, banana, orange, or pear 2 small apricots, kiwis, or plums 1 cup of diced or canned fruit (no sugar added)
Enjoy cooked seafood 2-3 times a week.
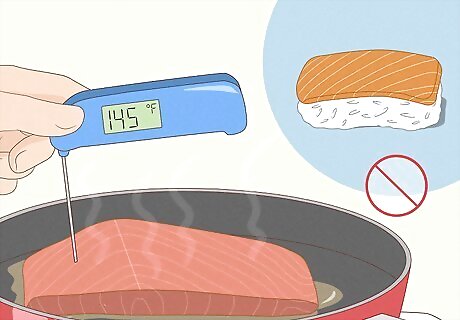
Fish contains high quality protein and many essential nutrients. Along with being protein-rich, fish are high in omega-3 fats which are important for heart and brain development. The most popular seafood (canned light tuna, tilapia, salmon, shrimp, catfish) have low mercury levels so they’re safe to consume. Don't eat more than 8-12 oz (226-340 g) of seafood weekly. Cook seafood until it reaches an internal temperature of 145 °F (63 °C). Avoid sushi, sashimi, raw oysters, and raw clams. Raw and undercooked seafood may contain parasites or bacteria, including Listeria, that could make you ill and potentially harm your baby. Avoid high-mercury fish like tilefish, shark, swordfish, and king mackerel. Mercury is a poisonous metal that is known to cause birth defects. An alternative to fish if you're vegan or vegetarian is to consume nuts, seeds, and avocados.
Up your daily calorie intake.
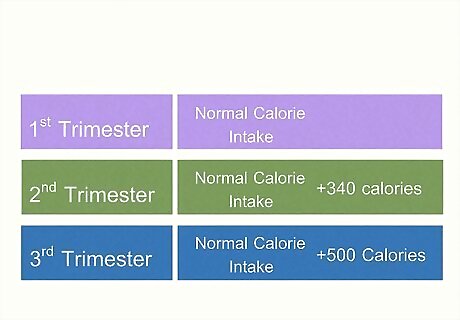
You need to increase your daily calories—but not by much. The phrase “eating for 2” gets thrown around a lot, but that doesn’t mean 2 adults! A growing fetus doesn’t require a lot of calories to grow healthy and strong. In fact, during your first trimester, you don’t need to increase your daily calorie intake at all. In your second trimester, add an extra 340 calories to your normal daily intake. In your third trimester, increase your normal intake by 500 calories. The recommended daily amount for females is 2,000 calories, but it varies depending on age, metabolism, physical activity, etc. For a more precise number, use an online calorie calculator (most are totally free and accurate). Once you figure out your needs, it’s important to actually eat at least that many calories every day. Restricted eating is not safe during pregnancy.
Meet your daily needs for key nutrients.

Calcium, folic acid, vitamin D, and iron are crucial nutrients. There’s a lot of confusing and conflicting information out there about nutrition during pregnancy. We’ve consulted trusted scientific sources to get hard facts about these key nutrients. Here’s what you need: Calcium: 1,000 mg daily for ages 19 and up. For teens: 1,300 mg daily. Good sources include milk, cheese, yogurt, broccoli, and kale. Folic acid: 400 mcg daily for the first 12 weeks, then 600 mcg daily until birth. Good sources include citrus fruits, leafy greens, beans, and cereals. Vitamin D: 600 IU (international units) daily. Good sources include fatty fish (like salmon) and fortified milk. Iron: 27 mg daily. Good sources include lean meat, leafy greens, beans, nuts, and raisins.
Ask your doctor about vitamins and supplements.
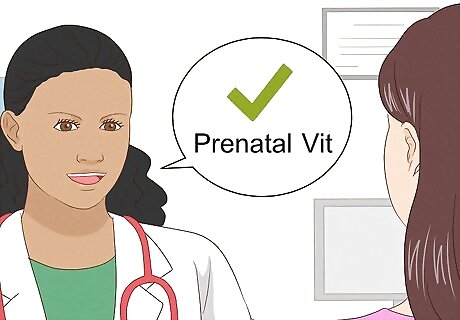
A balanced diet should meet your needs, but a prenatal vitamin can help. You’re probably juggling a lot right now and eating a perfectly balanced diet every single day is not easy! If you consistently aren’t fulfilling your nutritional needs from food, an OTC prenatal vitamin can help fill in the gaps. You don’t need to take any other special vitamins or supplements during your pregnancy (unless your doctor recommends them). Get the green light from your doctor before you start prenatal vitamins. Quality prenatal vitamins should include folic acid (600 mcg), iron (27 mg), and calcium (1,000 mg). Avoid herbal and botanical supplements. There’s no scientific evidence to support them and they may cause severe and detrimental side effects. You may have heard that you should take a calcium supplement, you don't need to as long as you're eating enough calcium-rich food. Studies have shown that your body’s capacity to absorb dietary calcium actually increases during pregnancy.
Limit your intake of certain foods.

Some foods aren't ideal but generally safe in small amounts. Most of these items aren’t great for you even when you aren’t pregnant, but you really want to pay attention during your pregnancy. There’s no known “safe amount” for any of these, but you can definitely talk to your doctor for recommendations and personal guidelines. In general, try to limit: Anything with caffeine (including food and beverages) Saturated fats Refined white sugar and sugary foods Added salt and high-sodium foods Packaged foods with lots of preservatives
Steer clear of a few foods entirely.

Certain foods are extra risky for pregnant people. These foods are risky for a variety of reasons: bacteria, viruses, potential birth defects, possible miscarriage, and so on. Here’s a general list of foods/beverages you should steer clear of: Alcohol Unpasteurized dairy items High mercury fish (tilefish, shark, swordfish, and king mackerel) Deli salads (tuna salad, chicken salad, ham salad) Soft cheeses like brie and ricotta (unless fully cooked and served hot) Refrigerated meat spreads like pate Raw and undercooked meat and seafood Raw eggs















Comments
0 comment