
views
Using the "Swapon" Command
Press Ctrl+Alt+T to open the Terminal. The Terminal is used in most Linux distributions to enter text commands. Press Ctrl + Alt + T to open the Terminal. Alternatively, you can open the terminal on most Linux distributions by opening the Apps menu and clicking the icon that resembles a black screen with a text cursor.
Type swapon and press ↵ Enter. This command displays the swap file usage in GB. Type "-s" after "swapon" to display the swap file size in kilobytes (KB) instead of gigabytes (GB).
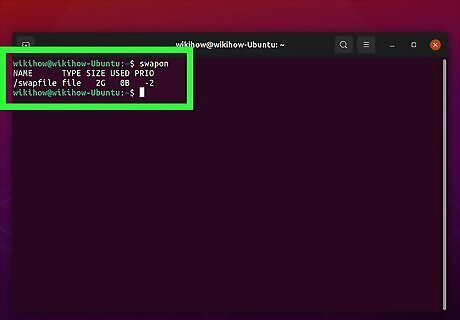
Check the command-line return. The command-line should display the total amount of swap space you have below "size." The total amount of swap space that is currently being used is displayed below "used."
Using the "Free" command
Press Ctrl+Alt+T to open the Terminal. The Terminal is used in most Linux distributions to enter text commands. Press Ctrl + Alt + T to open the Terminal. Alternatively, you can open the terminal on most Linux distributions by opening the Apps menu and clicking the icon that resembles a black screen with a text cursor.
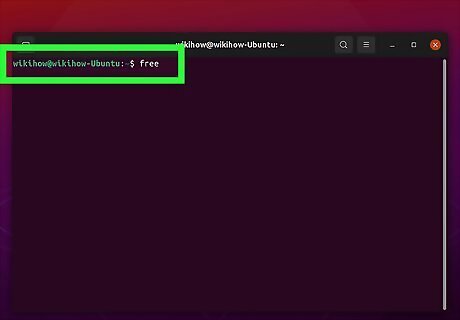
Type free and press ↵ Enter The "free" command will show both your memory and your swap space usage. Type "-h" after the "free" command to display the return output in 3-digit format. This will display the amount of memory and swap space you are using in gigabytes or megabytes, depending on how much memory and swap space you have. Type "-m" after the "free" command to display the return output in megabytes (MB) instead of kilobytes.
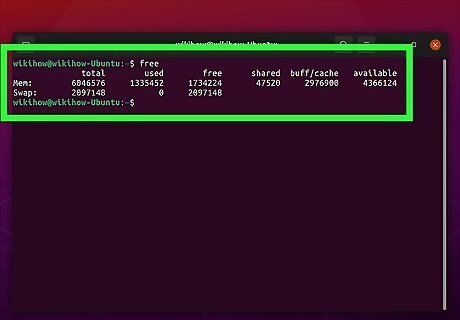
Check the command-line return. The "free" command displays how much memory and swap space you have in all below "total." The amount of memory and swap space you are currently using is displayed below "used." The amount of memory and swap space you have available is displayed below "available." The amount of swap space and memory you have is displayed in kilobytes (KB).
Using the "Cat" Command
Press Ctrl+Alt+T to open the Terminal. The Terminal is used in most Linux distributions to enter text commands. Press Ctrl + Alt + T to open the Terminal. Alternatively, you can open the terminal on most Linux distributions by opening the Apps menu and clicking the icon that resembles a black screen with a text cursor.
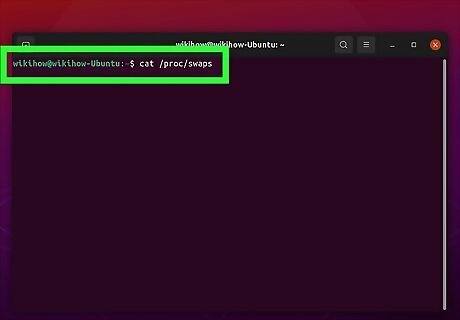
Type cat /proc/swaps and press ↵ Enter. The "cat" command is used to check the contents and size of a file in Linux. The location of the swap space file is usually "/proc/swaps." This command checks the file size and contents of the swap file.
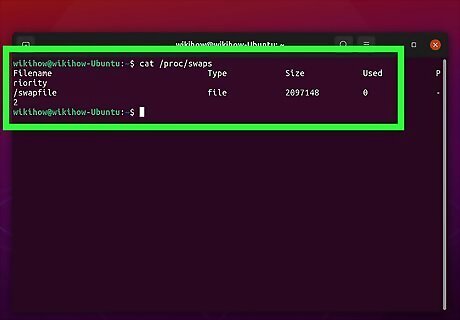
Check the command-line return. The overall size of the swap file is displayed in kilobytes (KB) below "size." The amount of swap space used is displayed in kilobytes below "used."
Using the "Top" Command
Press Ctrl+Alt+T to open the Terminal. The Terminal is used in most Linux distributions to enter text commands. Press Ctrl + Alt + T to open the Terminal. Alternatively, you can open the terminal on most Linux distributions by opening the Apps menu and clicking the icon that resembles a black screen with a text cursor.
Type top and press ↵ Enter. The "Top" command displays the status of a variety of Linux processes in real-time. This includes memory and swap space usage.
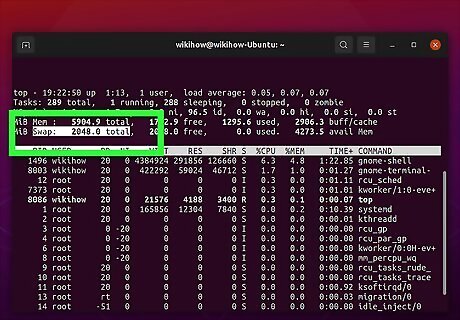
Check your swap space usage next to "Swap". It's at the top of the list of processes in the header section. You can see how much swap space you have total in megabytes (MB) to the right of "total." The amount of swap space you have available is displayed to the right of "free." The amount of swap space you are currently using is displayed next to the right of "used."
Press Q to quit. When you are ready to return the command-line prompt, press "Q" to quit Top.
Using the "VMstat" Command
Press Ctrl+Alt+T to open the Terminal. The Terminal is used in most Linux distributions to enter text commands. Press Ctrl + Alt + T to open the Terminal. Alternatively, you can open the terminal on most Linux distributions by opening the Apps menu and clicking the icon that resembles a black screen with a text cursor.
Type vmstat and press ↵ Enter. The "vmstat" command displays the status of your virtual memory. It doesn't display as much information as the previous commands, but you can use it to check how much swap space you are using as well as how much memory you are using.
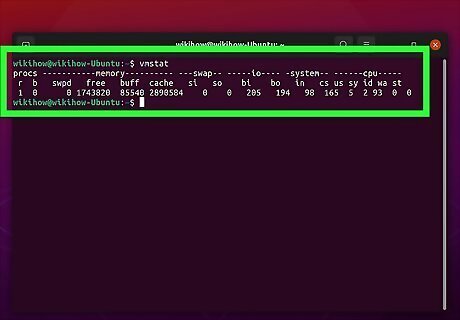
Check the amount of swap space you are using below "swpd." This displays how much swap space you are using in kilobytes (KB).




















Comments
0 comment