
views
Averaging Any Short Series of Consecutive Numbers
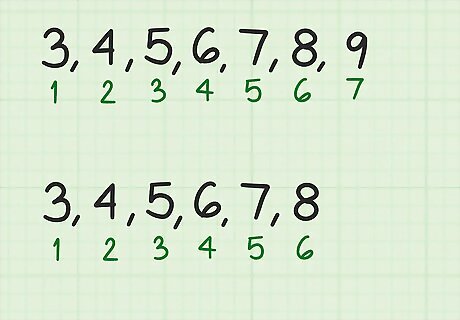
Count the number of terms in the series. This is the number of numbers in the sequence. Determine whether the series has an odd or even number of terms. For example, the sequence 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 has seven terms, an odd amount. The sequence 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 has six terms, an even amount.
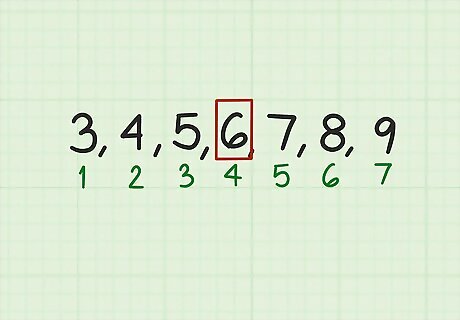
Identify the middle number of a series with an odd number of terms. This is the number that has the same amount of terms on either side of it. This middle number will be the average of the series. For example, in the sequence 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, the middle number is 6. It has three numbers to the left of it, and three numbers to the right of it. So, in this series of numbers, 6 is both the mean and the median.
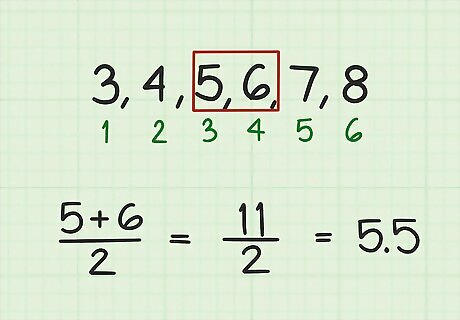
Average the middle numbers of a series with an even number of terms. To do this, find the pair of numbers that has the same amount of terms on either side of it. To find the average, add these two numbers together and divide by two. Their average will be the average of the series. For example, in the sequence 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, the middle pair is 5 and 6. It has two numbers to the left of it, and two numbers to the right of it. So, to calculate the average of the series, calculate the average of these two numbers: 5 + 6 2 = 11 2 = 5.5 {\displaystyle {\frac {5+6}{2}}={\frac {11}{2}}=5.5} {\frac {5+6}{2}}={\frac {11}{2}}=5.5So, in this series of numbers, 5.5 is both the mean and the median.
Averaging Any Long Series of Consecutive Numbers
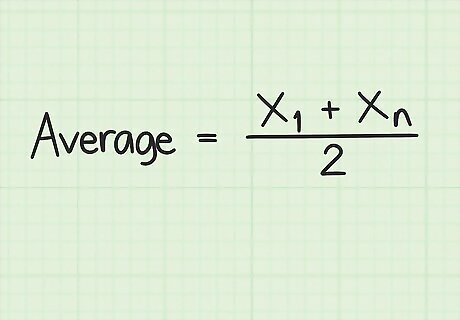
Set up the formula for finding the average of an evenly spaced set of numbers. The formula is Average = ( x 1 + x n ) 2 {\displaystyle {\text{Average}}={\frac {(x_{1}+x_{n})}{2}}} {\text{Average}}={\frac {(x_{{1}}+x_{{n}})}{2}}, where x 1 {\displaystyle x_{1}} x_{{1}} is the first number in the series and x n {\displaystyle x_{n}} x_{{n}} is the last number in the series.
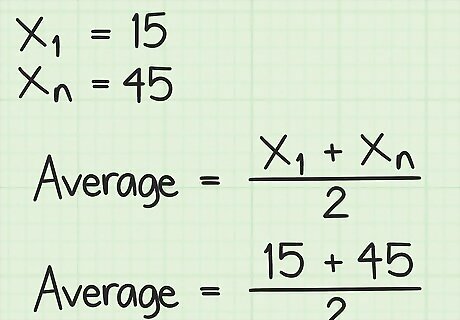
Plug the appropriate values into the formula. Remember, for this formula, you are only working with the first number in the sequence ( x 1 {\displaystyle x_{1}} x_{{1}}) and the last number in the sequence x n {\displaystyle x_{n}} x_{{n}}. For example, if you were finding the average of sequential numbers beginning with 15 and ending with 45, your formula will look like this: Average = ( 15 + 45 ) 2 {\displaystyle {\text{Average}}={\frac {(15+45)}{2}}} {\text{Average}}={\frac {(15+45)}{2}}.
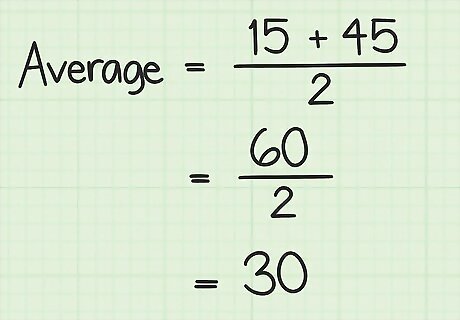
Calculate using the order of operations. First you need to add the two values in parentheses. Then divide by 2. The result will be the average of the series of numbers. For example: ( 15 + 45 ) 2 = 60 2 = 30 {\displaystyle {\frac {(15+45)}{2}}={\frac {60}{2}}=30} {\frac {(15+45)}{2}}={\frac {60}{2}}=30So, the average of the series of consecutive numbers beginning with 15 and ending with 45 is 30.
Averaging Any Consecutive Series Beginning with 1
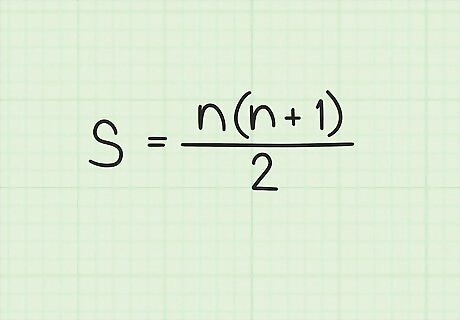
Set up the formula for calculating the sum of a series of consecutive numbers. The formula is S = n ( n + 1 ) 2 {\displaystyle S={\frac {n(n+1)}{2}}} S={\frac {n(n+1)}{2}}, where s {\displaystyle s} s equals the sum of all the numbers in the series, and n {\displaystyle n} n equals the number of terms (numbers) in the series.
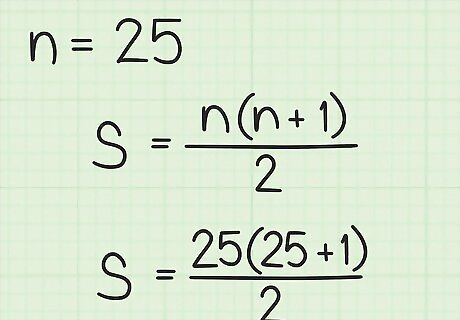
Count the number of terms in the series. Since the series begins with 1, the number of terms is equal to the last term in the series. Plug in this value for n {\displaystyle n} n. For example, if you are finding the sum of consecutive numbers 1 through 25, you have 25 numbers in your sequence, so n = 25 {\displaystyle n=25} n=25, and your formula will look like this: S = 25 ( 25 + 1 ) 2 {\displaystyle S={\frac {25(25+1)}{2}}} S={\frac {25(25+1)}{2}}.
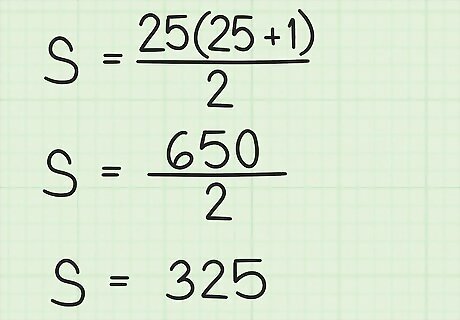
Calculate using the order of operations. First add the numbers in parentheses. Then, multiply their sum by n {\displaystyle n} n. Finally, divide the product by 2. The result is the sum of the numbers in the series. For example: S = 25 ( 26 ) 2 {\displaystyle S={\frac {25(26)}{2}}} S={\frac {25(26)}{2}} S = 650 2 {\displaystyle S={\frac {650}{2}}} S={\frac {650}{2}} S = 325 {\displaystyle S=325} S=325
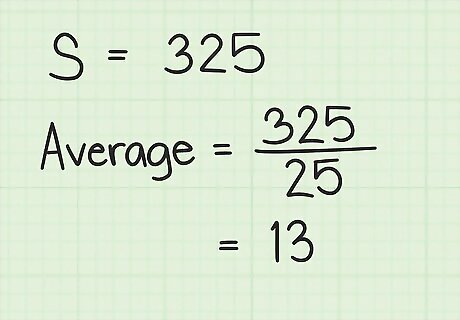
Divide the sum by the number of terms in the series. This will give you the average of the series. For example, 325 25 = 13 {\displaystyle {\frac {325}{25}}=13} {\frac {325}{25}}=13. So, the average of the series 1-25 is 13.
















Comments
0 comment