
views
X
Research source
Thankfully, it only takes a few minutes and some careful measuring to bring your bass back to peak playing condition!
Adjusting Your Bridge by Hand

Place the bass face-up on a flat, sturdy surface. Find a large, open space in your home or practice area where you can lay your double bass flat on the ground. Always keep the bridge and strings face-up so the instrument isn’t damaged. If you don’t have a lot of room in your home, place your bass on your bed.
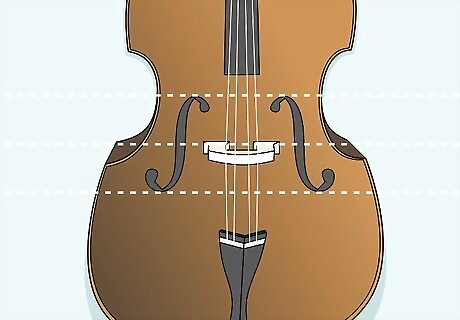
Check that your bridge lines up with the notches in the F holes. Take a close look at large, symmetrical F holes on both sides of your base. On the inner edge of each opening, look for a carefully etched notch—these notches form an invisible, horizontal line across your instrument, and represent where your bridge should be placed. Look at your bridge to see if it’s centered over this line, or if it needs to be adjusted. The F holes are the large, curvy openings on the front of your bass that resemble a cursive F. It’s okay if your bridge isn’t exactly straight—it’s easy to adjust!
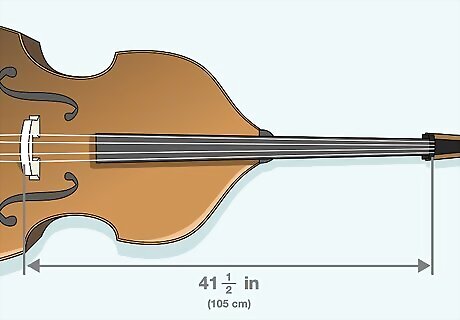
Measure the vibrating string length with a ruler. Check online or contact your luthier, or bass maker, and see what the vibrating length of your bass string is. Use this number as a guide when measuring the string from the tuning pegs down to the bridge. The vibrating length of the string is the ideal length of the string between the top of the instrument and the bridge. If this section of string is too short, then your bridge has shifted forward and needs to be readjusted. Some basses have a vibrating string length of about 41 ⁄2 in (105 cm).

Pinch the outside of the bridge with your thumb and middle finger. Grip the outside edges of your bridge firmly to hold it in place. Keep your arm and hand tucked beneath the strings so you don’t hurt your bass in the process.

Push the bridge with the thumb of your opposite hand. Place your fingers on top of the strings, centering your thumb next to the top of the bridge. Force the bridge backwards until it’s completely perpendicular to the base of the instrument. Don’t use your fingers to pinch and adjust the bridge. Using your thumb is an accurate way to adjust your instrument without possibly harming the bridge piece. Measure with a small ruler or other straight object to see if your bridge forms a 90-degree angle with the rest of the instrument.

Try to slide a small sheet of paper beneath the feet of your bridge. Place the paper flat on your instrument, then try to push it beneath the bridge feet. If your bridge is completely sturdy and well-adjusted, you won’t be able to slide the paper beneath the bridge whatsoever. If you can slide the paper beneath your bridge, you’ll need to make a few more adjustments.

Push on the bridge with your thumb to make any final adjustments. Use both hands to tweak and adjust the bridge. Double-check the string length against your ruler or measuring tape for extra confirmation.Tip: You can also measure out your bridge with a bridge stick, or piece of wood that helps measure the distance between your bridge and fingerboard. Use the bridge stick as a template to see if your fingerboard and bridge are spaced evenly. Some luthiers include a bridge stick with the double bass.
Using an Adjustable Bridge
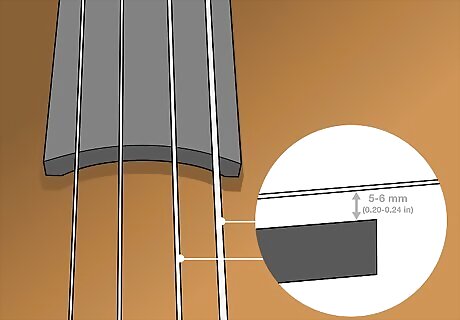
Check that the height of your “G” and “D” strings is 5 to 6 mm (0.20 to 0.24 in). Measure the gap between each bass string and the fingerboard. Keep in mind that the leftmost 2 strings (D and G), or the “G side” need to be 5 to 6 mm (0.20 to 0.24 in) above the fingerboard. This is a good measurement for solo bass music. If you’re using orchestral strings, you can raise your strings to 8 or 9 mm (0.31 or 0.35 in) above the fingerboard, depending on how the strings feel.
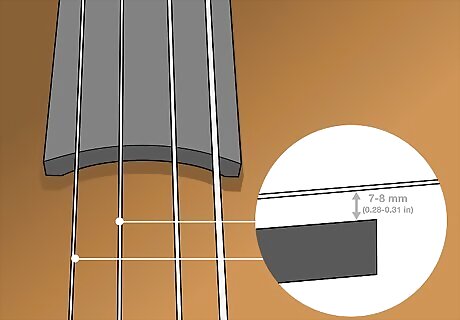
Measure your “E” and “A” strings to see if they’re 7 to 8 mm (0.28 to 0.31 in) high. Use a ruler to see how high your bass strings sit above the fingerboard. Check that your strings are around 7 to 8 mm (0.28 to 0.31 in) away from the fingerboard, or jot down what the current measurement is. Use your own discretion when adjusting your strings. If a certain measurement feels more comfortable, go with that. When your strings have more tension, they tend to sound brighter.
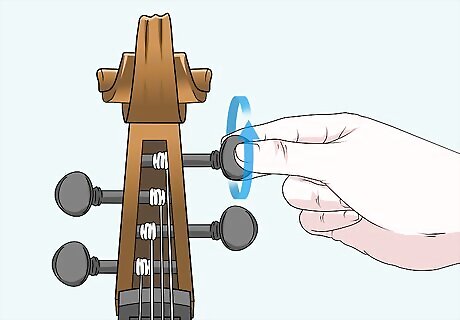
Loosen the tuning pegs before making any adjustments. Rotate your tuning pegs to the right to loosen the strings a little bit. You don’t need to loosen or unwind the strings all the way—just enough so your strings aren’t super tight and tense along the bridge. Unlike other string instruments, double basses use special pegs for tuning and string adjustments. Turn these pegs to the left to loosen the strings, and twist them to the right to tighten the strings.

Rotate the wheels on your bass bridge to raise or lower your strings. Look above the feet of your bridge to find adjustable metal rings. Test out these rings by turning them slightly, and see if your bridge goes up or down. Use these wheels as needed to lift and lower your strings along your bridge.
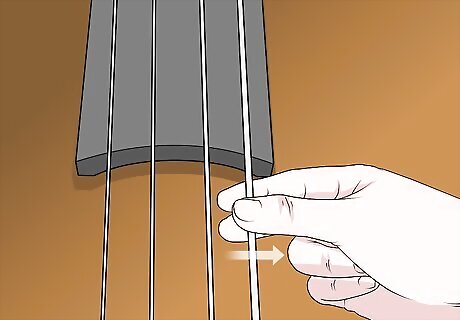
Double-check and tweak your string height before you play. Measure between the string and the fingerboard to see how high your strings are hovering. If they seem a bit too high or low, make a few final adjustments with your bridge until you’re happy with the string height.
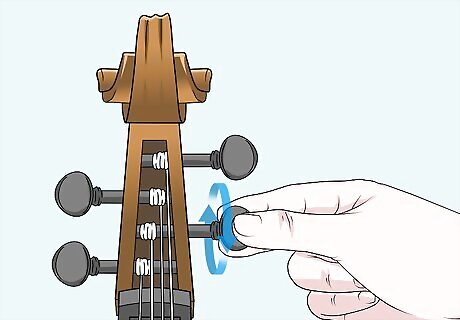
Tighten and re-tune the strings so you can play your bass. Rotate the machine pegs counter clockwise to tighten the strings and add more tension to the instrument. Check that each string is in tune with a digital tuner so you can get back to playing your double bass!


















Comments
0 comment