
views
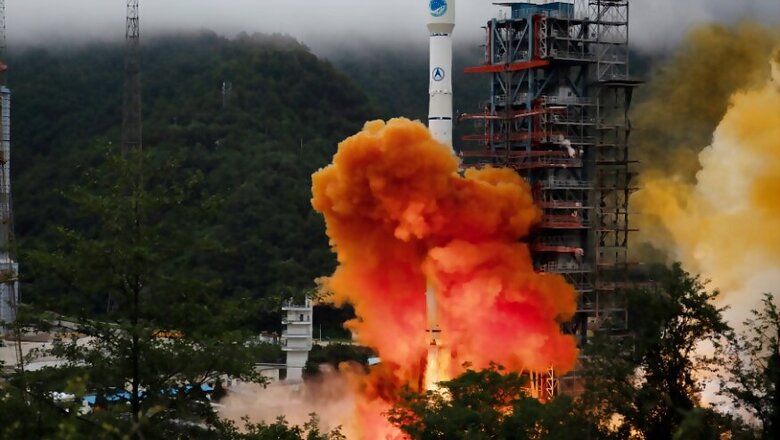
China on Tuesday launched the latest satellite of its Beidou geo-location system (BDS), its alternative to the American GPS. The launch, from the base of Xichang in Sichuan province, took place at 9.43 a.m., on the "Long March 3B" transport rocket, Efe news reported.
The satellite, which successfully entered orbit 25 minutes later, will complete the network of 35 third-generation devices (BDS-3) of the Beidou system (Big Dipper in Chinese), which the Asian country launched in 2015 to be able to offer coverage global positioning. The launch of the last satellite was scheduled for June 16, but was suspended for "technical reasons".
China began building the Beidou 20 years ago, with the aim of being self-sufficient in navigation technology and having an alternative system to GPS. It is made up of two separate satellite constellations. The Beidou-1 consists of three satellites that since 2000 have offered limited coverage and navigation and positioning services for China and some neighbouring countries.
The Beidou-2 began operating in December 2011 with ten satellites in orbit and has offered navigation and positioning services to the countries of the Asia-Pacific region. With the Beidou-3, the system would reach global coverage this year and would be ready to provide an alternative to the other three currently in existence: the American GPS, the European Galileo and the Russian GLONASS. With 35 satellites, Beidou would have more than 31 in the US system and also more than the European and Russian systems. Nearly 200 countries have already applied to China for BDS technologies, which it currently exports to more than 120 nations.


















Comments
0 comment