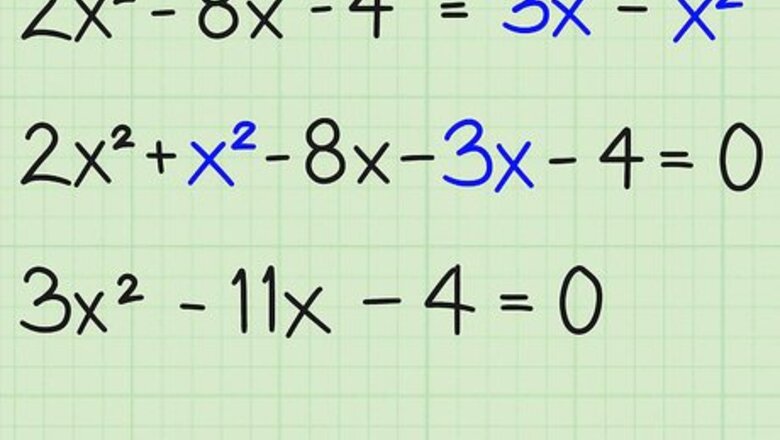
views
X
Research source
There are three main ways to solve quadratic equations: 1) to factor the quadratic equation if you can do so, 2) to use the quadratic formula, or 3) to complete the square. If you want to know how to master these three methods, just follow these steps.
Factoring the Equation
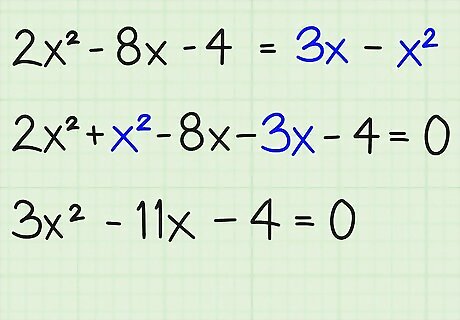
Combine all of the like terms and move them to one side of the equation. The first step to factoring an equation is to move all of the terms to one side of the equation, keeping the x 2 {\displaystyle x^{2}} x^{2} term positive. To combine the terms, add or subtract all of the x 2 {\displaystyle x^{2}} x^{2} terms, the x {\displaystyle x} x terms, and the constants (integer terms), moving them to one side of the equation so that nothing remains on the other side. Once the other side has no remaining terms, you can just write "0" on that side of the equal sign. Here's how you do it: 2 x 2 − 8 x − 4 = 3 x − x 2 {\displaystyle 2x^{2}-8x-4=3x-x^{2}} 2x^{2}-8x-4=3x-x^{2} 2 x 2 + x 2 − 8 x − 3 x − 4 = 0 {\displaystyle 2x^{2}+x^{2}-8x-3x-4=0} 2x^{2}+x^{2}-8x-3x-4=0 3 x 2 − 11 x − 4 = 0 {\displaystyle 3x^{2}-11x-4=0} 3x^{2}-11x-4=0
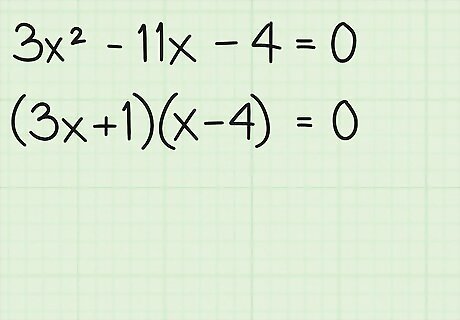
Factor the expression. To factor the expression, you have to use the factors of the x 2 {\displaystyle x^{2}} x^{2} term (3), and the factors of the constant term (-4), to make them multiply and then add up to the middle term, (-11). Here's how you do it: Since 3 x 2 {\displaystyle 3x^{2}} 3x^{2} only has one set of possible factors, 3 x {\displaystyle 3x} 3x and x {\displaystyle x} x, you can write those in the parenthesis: ( 3 x ± ? ) ( x ± ? ) = 0 {\displaystyle (3x\pm ?)(x\pm ?)=0} (3x\pm ?)(x\pm ?)=0. Then, use the process of elimination to plug in the factors of 4 to find a combination that produces -11x when multiplied. You can either use a combination of 4 and 1, or 2 and 2, since both of those numbers multiply to get 4. Just remember that one of the terms should be negative, since the term is -4. By trial and error, try out this combination of factors ( 3 x + 1 ) ( x − 4 ) {\displaystyle (3x+1)(x-4)} (3x+1)(x-4). When you multiply them out, you get 3 x 2 − 12 x + x − 4 {\displaystyle 3x^{2}-12x+x-4} 3x^{2}-12x+x-4. If you combine the terms − 12 x {\displaystyle -12x} -12x and x {\displaystyle x} x, you get − 11 x {\displaystyle -11x} -11x, which is the middle term you were aiming for. You have just factored the quadratic equation. As an example of trial and error, let's try checking a factoring combination for 3 x 2 − 11 x − 4 = 0 {\displaystyle 3x^{2}-11x-4=0} 3x^{2}-11x-4=0 that is an error (does not work): ( 3 x − 2 ) ( x + 2 ) {\displaystyle (3x-2)(x+2)} (3x-2)(x+2) = 3 x 2 + 6 x − 2 x − 4 {\displaystyle 3x^{2}+6x-2x-4} 3x^{2}+6x-2x-4. If you combine those terms, you get 3 x 2 − 4 x − 4 {\displaystyle 3x^{2}-4x-4} 3x^{2}-4x-4. Though the factors -2 and 2 do multiply to make -4, the middle term does not work, because you needed to get − 11 x {\displaystyle -11x} -11x, not − 4 x {\displaystyle -4x} -4x.
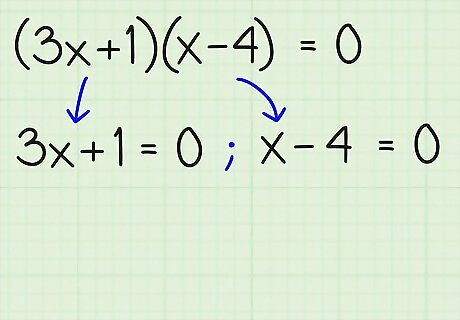
Set each set of parenthesis equal to zero as separate equations. This will lead you to find two values for x {\displaystyle x} x that will make the entire equation equal to zero, ( 3 x + 1 ) ( x − 4 ) {\displaystyle (3x+1)(x-4)} (3x+1)(x-4) = 0. Now that you've factored the equation, all you have to do is put the expression in each set of parenthesis equal to zero. But why? -- because to get zero by multiplying, we have the "principle, rule or property" that one factor must be zero, then at least one of the factors in parentheses, as ( 3 x + 1 ) ( x − 4 ) {\displaystyle (3x+1)(x-4)} (3x+1)(x-4) must be zero; so, either (3x + 1) or else (x - 4) must equal zero. So, you would write 3 x + 1 = 0 {\displaystyle 3x+1=0} 3x+1=0 and also x − 4 = 0 {\displaystyle x-4=0} x-4=0.
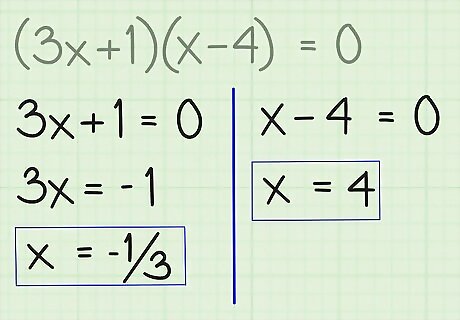
Solve each "zeroed" equation independently. In a quadratic equation, there will be two possible values for x. Find x for each possible value of x one by one by isolating the variable and writing down the two solutions for x as the final solution. Here's how you do it: Solve 3x + 1 = 0 3x = -1 ..... by subtracting 3x/3 = -1/3 ..... by dividing x = -1/3 ..... simplified Solve x - 4 = 0 x = 4 ..... by subtracting x = (-1/3, 4) ..... by making a set of possible, separate solutions, meaning x = -1/3, or x = 4 seem good.
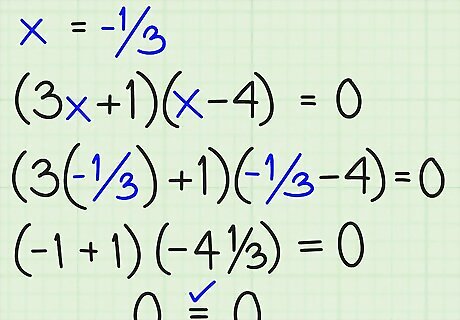
Check x = -1/3 in (3x + 1)(x – 4) = 0: We have (3[-1/3] + 1)([-1/3] – 4) ?=? 0 ..... by substituting (-1 + 1)(-4 1/3) ?=? 0 ..... by simplifying (0)(-4 1/3) = 0 ..... by multiplying therefore 0 = 0 ..... Yes, x = -1/3 works
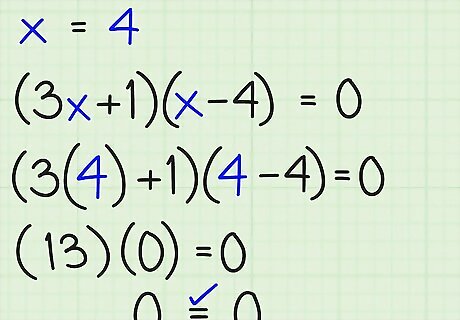
Check x = 4 in (3x + 1)(x - 4) = 0: We have (3[4] + 1)([4] – 4) ?=? 0 ..... by substituting (13)(4 – 4) ?=? 0 ..... by simplifying (13)(0) = 0 ..... by multiplying 0 = 0 ..... Yes, x = 4 works So, both solutions do "check" separately, and both are verified as working and correct for two different solutions.
Using the Quadratic Formula
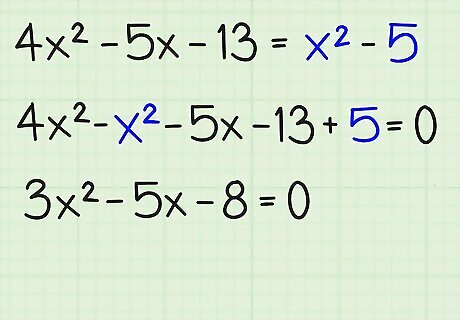
Combine all of the like terms and move them to one side of the equation. Move all of the terms to one side of the equal sign, keeping the x 2 {\displaystyle x^{2}} x^{2} term positive. Write the terms in descending order of degrees, so that the x 2 {\displaystyle x^{2}} x^{2} term comes first, followed by the x {\displaystyle x} x term and the constant term. Here's how you do it: 4x - 5x - 13 = x -5 4x - x - 5x - 13 +5 = 0 3x - 5x - 8 = 0
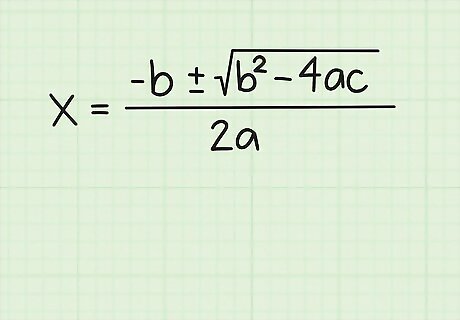
Write down the quadratic formula. The quadratic formula is: − b ± b 2 − 4 a c 2 a {\displaystyle {\frac {-b\pm {\sqrt {b^{2}-4ac}}}{2a}}} {\frac {-b\pm {\sqrt {b^{2}-4ac}}}{2a}}
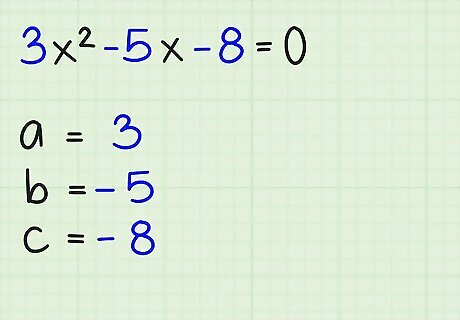
Identify the values of a, b, and c in the quadratic equation. The variable a is the coefficient of the x term, b is the coefficient of the x term, and c is the constant. For the equation 3x -5x - 8 = 0, a = 3, b = -5, and c = -8. Write this down.
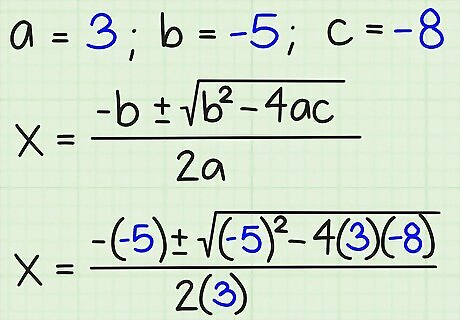
Substitute the values of a, b, and c into the equation. Now that you know the values of the three variables, you can just plug them into the equation like this: {-b +/-√ (b - 4ac)}/2 {-(-5) +/-√ ((-5) - 4(3)(-8))}/2(3) = {-(-5) +/-√ ((-5) - (-96))}/2(3)
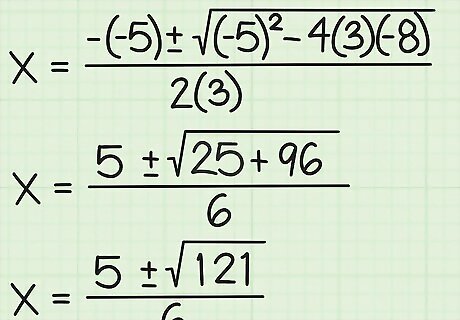
Do the math. After you've plugged in the numbers, do the remaining math to simplify positive or negative signs, multiply, or square the remaining terms. Here's how you do it: {-(-5) +/-√ ((-5) - (-96))}/2(3) = {5 +/-√(25 + 96)}/6 {5 +/-√(121)}/6
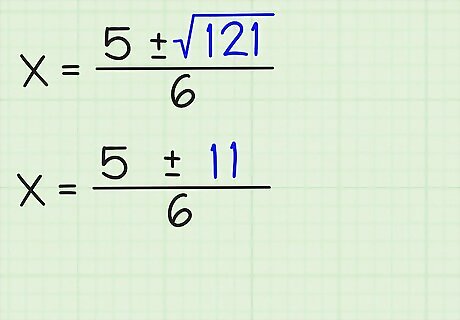
Simplify the square root. If the number under the radical symbol is a perfect square, you will get a whole number. If the number is not a perfect square, then simplify to its simplest radical version. If the number is negative, and you're sure it's supposed to be negative, then the roots will be complex. In this example, √(121) = 11. You can write that x = (5 +/- 11)/6.
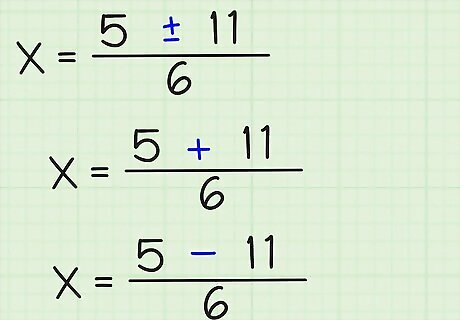
Solve for the positive and negative answers. If you've eliminated the square root symbol, then you can keep going until you've found the positive and negative results for x. Now that you have (5 +/- 11)/6, you can write two options: (5 + 11)/6 (5 - 11)/6
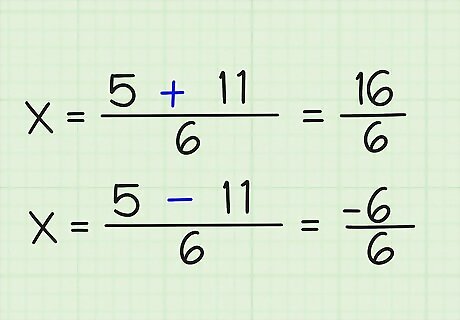
Solve for the positive and negative answers. Just do the math: (5 + 11)/6 = 16/6 (5-11)/6 = -6/6
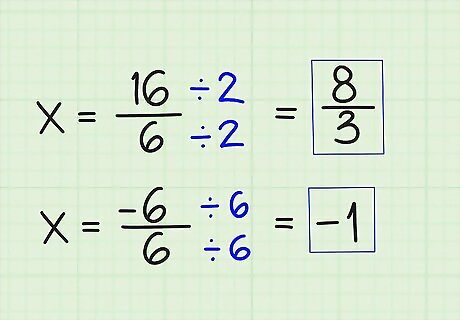
Simplify. To simplify each answer, just divide them by the largest number that is evenly divisible into both numbers. Divide the first fraction by 2, and divide the second by 6, and you have solved for x. 16/6 = 8/3 -6/6 = -1 x = (-1, 8/3)
Completing the Square
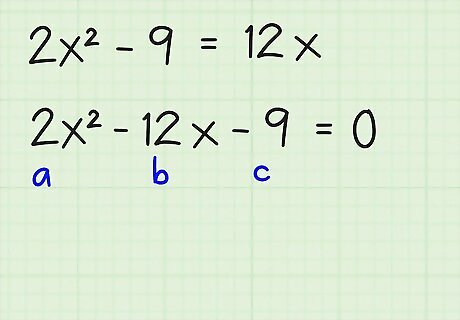
Move all of the terms to one side of the equation. Make sure that the a or x term is positive. Here's how you do it: 2x - 9 = 12x = 2x - 12x - 9 = 0 In this equation, the a term is 2, the b term is -12, and the c term is -9.
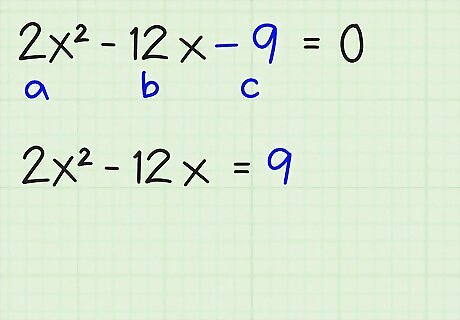
Move the c term or constant to the other side. The constant term is the numerical term without a variable. Move it to the right side of the equation: 2x - 12x - 9 = 0 2x - 12x = 9
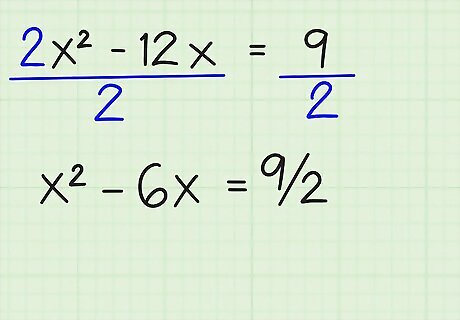
Divide both sides by the coefficient of the a or x term. If x has no term in front of it, and just has a coefficient of 1, then you can skip this step. In this case, you'll have to divide all of the terms by 2, like so: 2x/2 - 12x/2 = 9/2 = x - 6x = 9/2
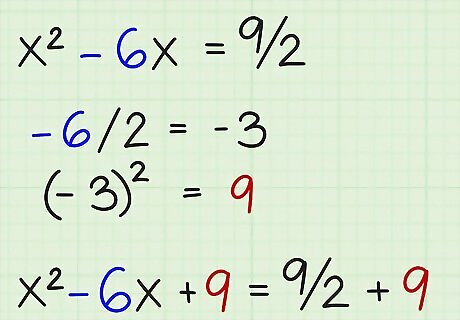
Divide b by two, square it, and add the result to both sides. The b term in this example is -6. Here's how you do it: -6/2 = -3 = (-3) = 9 = x - 6x + 9 = 9/2 + 9
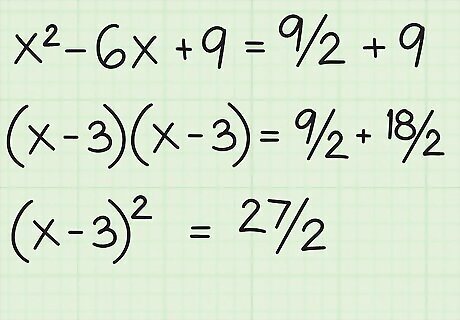
Simplify both sides. Factor the terms on the left side to get (x-3)(x-3), or (x-3). Add the terms on the right side to get 9/2 + 9, or 9/2 + 18/2, which adds up to 27/2.
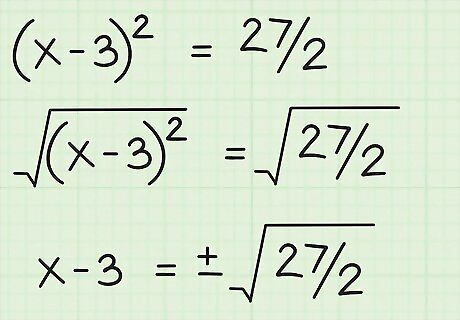
Find the square root of both sides. The square root of (x-3) is simply (x-3). You can write the square root of 27/2 as ±√(27/2). Therefore, x - 3 = ±√(27/2).
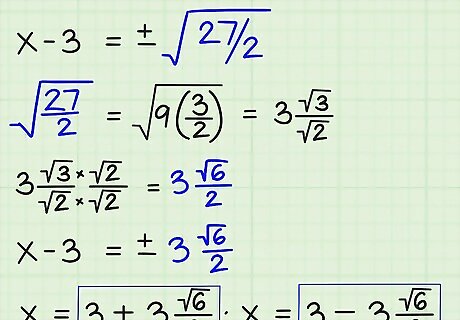
Simplify the radical and solve for x. To simplify ±√(27/2), look for a perfect square within the numbers 27 or 2 or in their factors. The perfect square 9 can be found in 27, because 9 x 3 = 27. To take 9 out of the radical sign, pull out the number 9 from the radical, and write the number 3, its square root, outside the radical sign. Leave 3 in the numerator of the fraction under the radical sign, since that factor of 27 cannot be taken out, and leave 2 on the bottom. Then, move the constant 3 on the left side of the equation to the right, and write down your two solutions for x: x = 3 + 3(√6)/2 x = 3 - 3(√6)/2)




















Comments
0 comment