views
Examining the Spider's Appearance
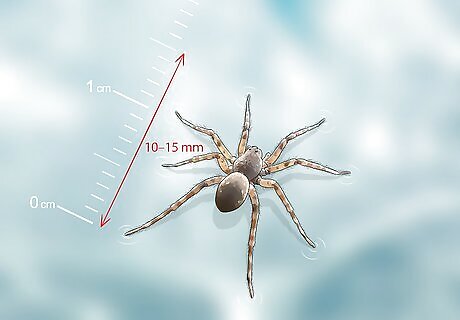
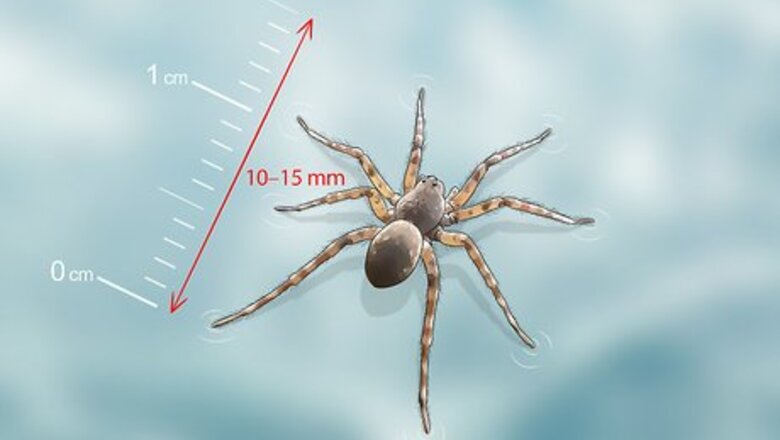
Check that the spider is 10–15 mm (0.39–0.59 in) in length. Water spiders are very small and most individuals tend to be within this range. However, male water spiders have been found to be from 7.8 to 18.7 mm (0.31 to 0.74 in) and female spiders from 7.8 to 13.1 mm (0.31 to 0.52 in). Male water spiders tend to be larger than the females because males spend more time hunting, which requires greater strength to overcome the resistance of the water. On the other hand, females tend to spend more time maintaining their webs.
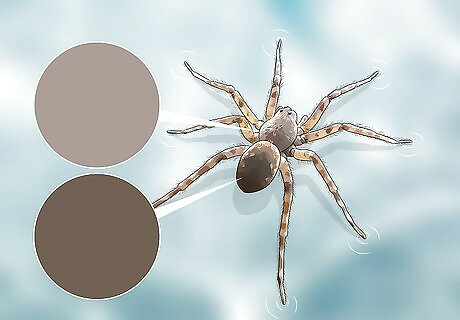
Look for a brown and velvety body. Water spiders have a head and thorax that is either light or dark brown. The abdomen tends to be dark brown and velvety in appearance. Sometimes water spiders can have a silvery appearance. This is because of the air bubble.

Observe a large bubble that is connected to the spider. Water spiders have a large air bubble connected to their abdomen. This enables them to breathe underwater. The bubble is made from the air that is trapped in the tiny hairs that cover the spider’s legs and abdomen. The bubble stays connected to the spider for the whole time it is underwater, even while the spider is swimming and hunting.
Observing the Spider's Environment and Behavior
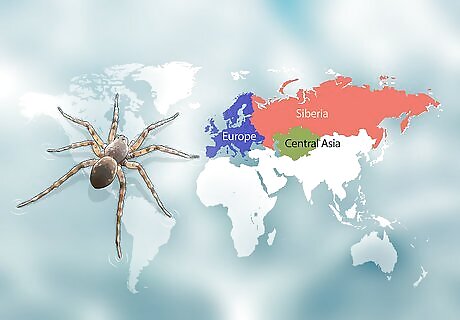
Know that water spiders are found in Europe, Siberia, and Asia. Geographically, water spiders are predominantly found in Central Asia, and Central and Northern Europe. You won't find water spiders in the USA, Canada, South America, Africa, or in the Pacific.

Check for a freshwater aquatic environment. Common habitats for water spiders include lakes, marshes, streams, ponds, and swamps. Water spiders tend to live in places where the water is slow-moving. Water spiders are particularly common in areas with a lot of aquatic vegetation.

See if the spider spends the majority of the day underwater. Water spiders are the only species of spider that live underwater. The spiders travel to the surface of the water approximately once per day for oxygen. All other activities, such as hunting and breeding, occur underwater. The bubble that is connected to the spider has nitrogen inside it which causes it to shrink over time. The spider will resurface to create a new bubble.


















Comments
0 comment