views
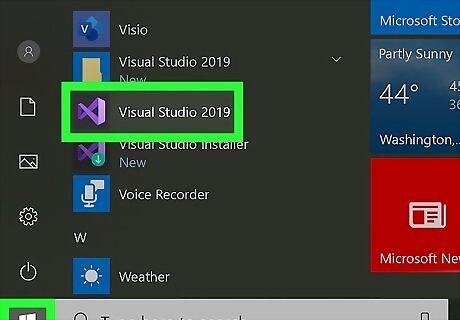
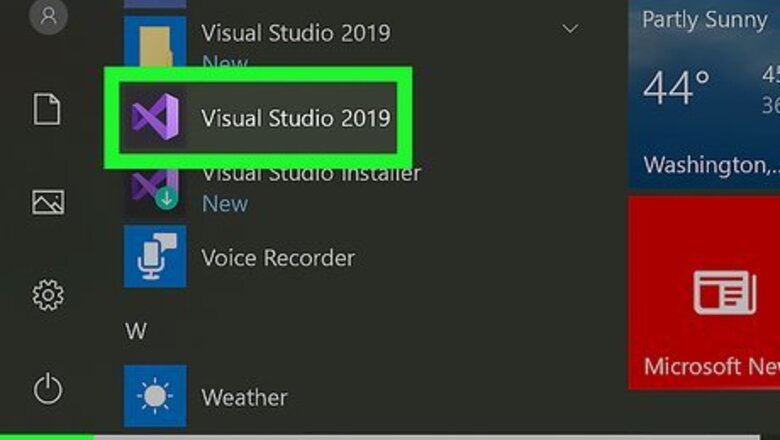
Open Visual Studio. You can find this in your Start Menu or Applications folder. Since a DLL is a library of information, it is only one piece of a project, and usually requires an accompanying app to access it. You can get Visual Studio for Windows here: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/visualstudio/install/install-visual-studio?view=vs-2019 Visual Studio for Mac can be downloaded here: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/visualstudio/mac/installation?view=vsmac-2019 This wikiHow will be using code provided by Microsoft to explain how to build a DLL file.
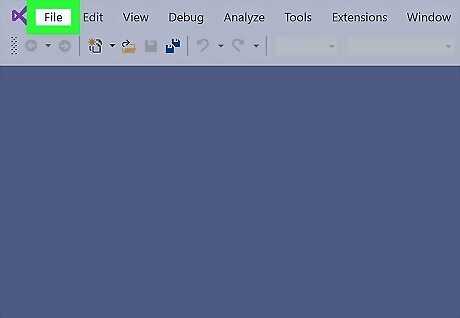
Click the File. You’ll find this either above the project space (Windows) or along the top of your screen (Macs).
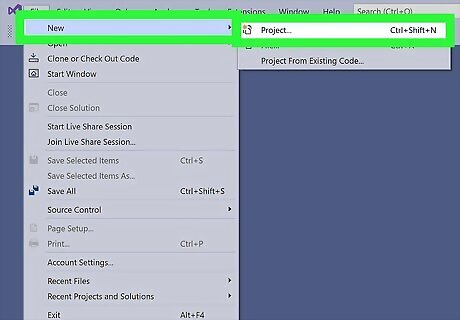
Click New and Project. The “Create a New Project” dialog box will pop up.
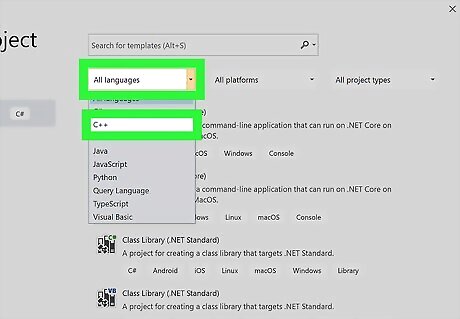
Set the options for Language, Platform, and Project Type. These will filter what kinds of project templates appear. Click Language to get a drop-down menu and click C++.
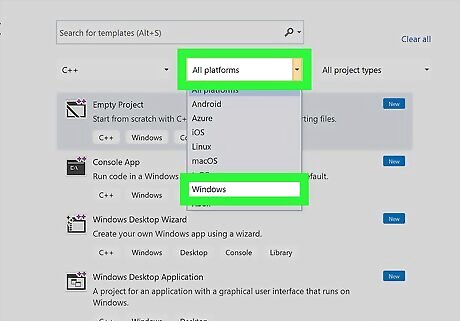
Click Platform to get a drop-down menu and click Windows.
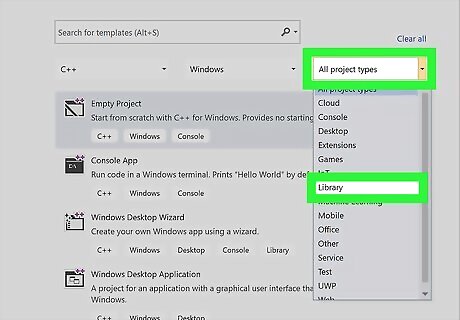
Click Project Type to get a drop-down menu and click Library.
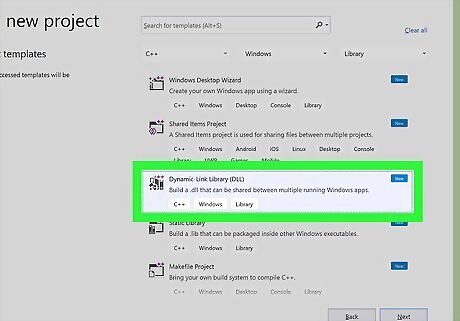
Click Dynamic-link Library (DLL). Your choice will highlight blue. Click Next to continue.
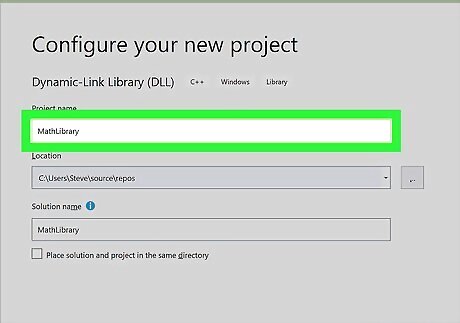
Type a name in the Name Box for the project. For example, type “MathLibrary” in the box for a sample name.
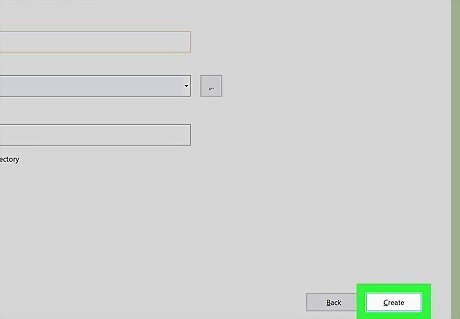
Click Create. The DLL project is created.
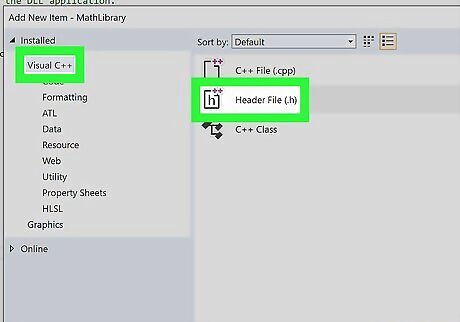
Add a header file to the DLL. You can do this by clicking “Add New Item” from “Project” in the menu bar. Select Visual C++ from the left menu of the dialog box. Select Header file (.h) from the center of the dialog box. Type the name as “MathLibrary.h” in the name field below the menu choices. Click Add to generate the blank header file.
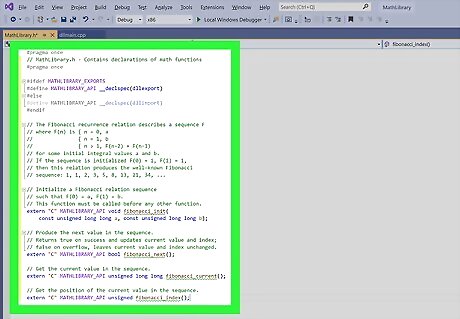
Type the following code into the blank header file. // MathLibrary.h - Contains declarations of math functions #pragma once #ifdef MATHLIBRARY_EXPORTS #define MATHLIBRARY_API __declspec(dllexport) #else #define MATHLIBRARY_API __declspec(dllimport) #endif // The Fibonacci recurrence relation describes a sequence F // where F(n) is { n = 0, a // { n = 1, b // { n > 1, F(n-2) + F(n-1) // for some initial integral values a and b. // If the sequence is initialized F(0) = 1, F(1) = 1, // then this relation produces the well-known Fibonacci // sequence: 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, ... // Initialize a Fibonacci relation sequence // such that F(0) = a, F(1) = b. // This function must be called before any other function. extern "C" MATHLIBRARY_API void fibonacci_init( const unsigned long long a, const unsigned long long b); // Produce the next value in the sequence. // Returns true on success and updates current value and index; // false on overflow, leaves current value and index unchanged. extern "C" MATHLIBRARY_API bool fibonacci_next(); // Get the current value in the sequence. extern "C" MATHLIBRARY_API unsigned long long fibonacci_current(); // Get the position of the current value in the sequence. extern "C" MATHLIBRARY_API unsigned fibonacci_index(); This is sample code provided from the Microsoft help website.
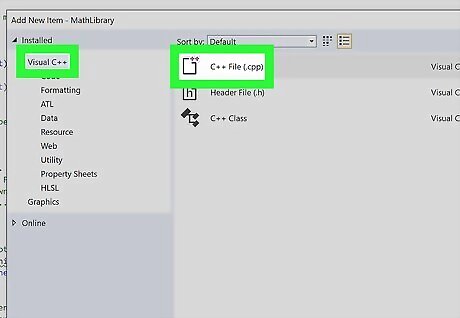
Add a CPP file to the DLL. You can do this by clicking Add New Item from “Project” in the menu bar. Select “Visual C++” from the left menu of the dialog box. Select “C++ File (.cpp)” from the center of the dialog box. Type the name as “MathLibrary.cpp” in the name field below the menu choices. Click Add to generate the blank file.
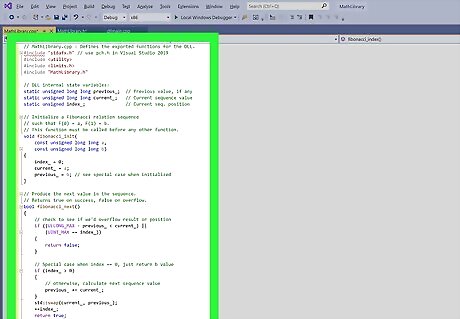
Type the following code into the blank file.
// MathLibrary.cpp : Defines the exported functions for the DLL.
#include "stdafx.h" // use pch.h in Visual Studio 2019
#include
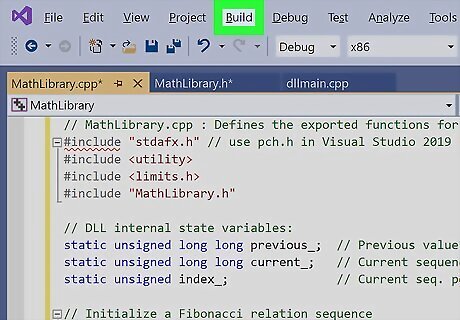
Click Build in the menu bar. You’ll find this either above the project space (Windows) or along the top of your screen (Macs).
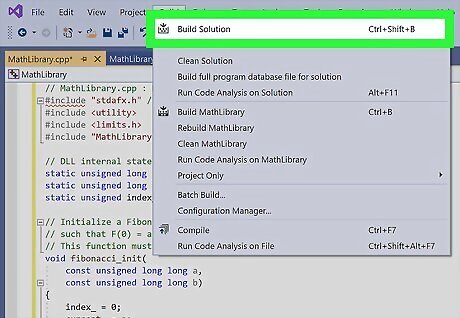
Click Build Solution. After you click that, you should see text similar to this: 1>------ Build started: Project: MathLibrary, Configuration: Debug Win32 ------ 1>MathLibrary.cpp 1>dllmain.cpp 1>Generating Code... 1> Creating library C:\Users\username\Source\Repos\MathLibrary\Debug\MathLibrary.lib and object C:\Users\username\Source\Repos\MathLibrary\Debug\MathLibrary.exp 1>MathLibrary.vcxproj -> C:\Users\username\Source\Repos\MathLibrary\Debug\MathLibrary.dll 1>MathLibrary.vcxproj -> C:\Users\username\Source\Repos\MathLibrary\Debug\MathLibrary.pdb (Partial PDB) ========== Build: 1 succeeded, 0 failed, 0 up-to-date, 0 skipped ========== If your DLL creation was successful, you'll see that here. If there was an error, it will be listed here for you to fix.















Comments
0 comment