
views
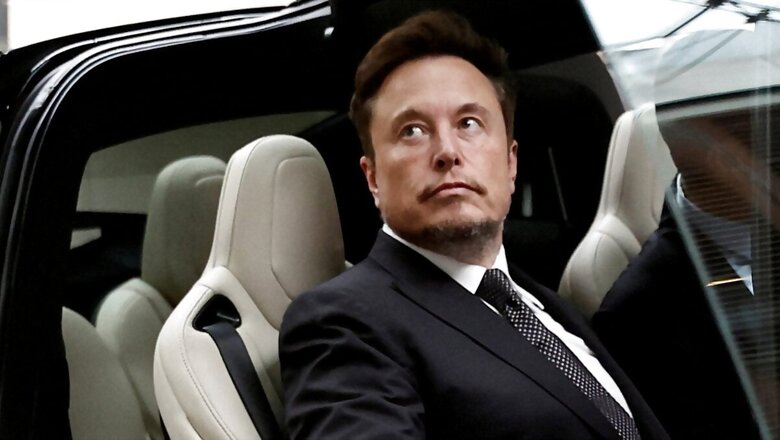
Elon Musk’s surprise visit to China on April 28, after he cancelled his much-anticipated trip to India, citing “very heavy Tesla obligations”, has won him approval for introducing Full Self-Driving (FSD) in Beijing.
Musk was scheduled to meet Prime Minister Narendra Modi and founders of an Indian space startup. The Tesla CEO was expected to announce a $2-3 billion Electric Vehicle (EV) factory for India during his visit with some announcements related to Starlink.
But on Sunday, Musk met with China’s Prime Minister Li Qiang and made promise towards rolling out the FSD in the world’s biggest automobile market.
What Was Discussed in China?
The Wall Street Journal reported that Beijing gave preliminary approval to Tesla to launch FSD in China. Tesla’s cars made in China passed key data security and privacy requirement in China. Previously, Tesla vehicles had faced bans from Chinese military installations and government sites over the issue of data collection.
This has given a much-needed boost to Tesla, which is struggling with slow EV demand in the US and FSD-related apprehensions in its home market. Tesla is also grappling with low sales in China where homegrown car manufacturers are providing competition to Musk’s company.
Chinese state broadcaster also reported that Tesla is likely to continue teaming up with tech company Baidu, which licences mapping data and its lane-level navigation service for FSD. Tesla has been using Baidu for in-car mapping and navigation since 2020.
Reuters also reported, a prominent Chinese automotive association confirmed on Sunday that Tesla’s Model 3 and Model Y vehicles were among the models subjected to testing and deemed compliant with China’s data security standards.
Reuters also reported, a prominent Chinese automotive association confirmed on Sunday that Tesla’s Model 3 and Model Y vehicles were subject to testing and deemed compliant with China’s data security standards.
On Tesla’s April 23 earnings call, Musk had said the EV major aims to release FSD “as a supervised autonomy system in any market that — where we can get regulatory approval for that, which we think includes China.”
Tesla has sold more than 1.7 million cars in China since it entered the market a decade ago and its Shanghai factory is its largest globally.
Roadblocks Between China and Tesla
China is Tesla’s second biggest market after US. Since 2021, Chinese officials have required Tesla to keep all data that its cars collect in China stored in Shanghai. This means, Tesla cannot send the data back to the US.
Data security and compliance were the biggest reasons why the US electric car company did not roll out the FSD in China yet despite launching its most advanced autopilot software four years ago.
Also, Chinese new energy car manufacturers such as BYD, Lotus, Nezha, Li Auto and Nio have already met the country’s stringent data security policy, which posed a tough competition to Tesla.
Tesla’s global vehicle deliveries experienced a decline in the first quarter, marking the first decrease in nearly four years.
According to a New York Times report, “Musk’s fortune is tied to Tesla’s Shanghai factory. The Shanghai factory has replaced Tesla’s plant in Fremont, California, as its largest and most productive, accounting for over half of the company’s global deliveries and the bulk of its profits”.
Meanwhile, a Wall Street Journal report said, “Musk’s response to the pressure has been to become a high-profile cheerleader of China’s ruling Communist Party, in sharp contrast to his renegade persona in the US, where he has clashed with the Securities and Exchange Commission and mocked President Biden in tweets, once calling him a labor union sock puppet”.
What is FSD Technology?
FSD is the most autonomous version of Autopilot software and was rolled out in 2020. Its features include self-parking, auto lane changes and traffic navigations. But Tesla say FSD or Autopilot does not make it vehicles autonomous and they require active driver supervision.
Each Tesla vehicle is equipped with multiple external cameras and vision processing software, which the company uses to deliver Autopilot features – an advanced driver assistance system or ADAS.
Autopilot includes what Tesla calls ‘Traffic-Aware Cruise Control’, which matches the speed of the vehicle to that of the surrounding traffic, and ‘Autosteer’, a function that assists in steering within a clearly marked lane, and uses traffic-aware cruise control. FSD, however, is a further upgrade to Autopilot that was launched in 2020 and aims at a driving experience involving minimal driver intervention.
In 2023, Musk said the price of FSD, then at $15,000, was very low, saying the value of the car would increase dramatically if it became autonomous. Last month, Tesla slashed the price of FSD to $8,000 from $12,000 in the US.
Disadvantages of FSD
Problems range from jumping red lights, not recognising pedestrians to situational problems like identifying a cyclist who briefly disappears behind a parked vehicle. Tesla began beta testing its full self-driving system only in 2020.
Google’s Waymo and Cruise owned by General Motors are among companies that predicted full self-driving cars by 2020, with only limited success: that too limited to ring fenced, geotagged areas.
Tesla relies primarily on car cameras, while humans make predictions based on road situation, which can present a complex problem for computers, such as when someone at the side of the road steps off the pavement and disappears behind a parked bus for a minute or distinguishing between a red signage on a wall versus an actual stop sign, as mentioned in The Indian Express.
The National Highway Transportation Safety Administration had said it was opening a new probe of Tesla self-driving systems amid concerns that a move last year to improve driver monitoring and attention was not up to the mark.


















Comments
0 comment